Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects of phonophoresis in animal models: a randomized experimental study
- PMID: 30698227
- PMCID: PMC6345359
- DOI: 10.1590/1414-431X20187773
Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects of phonophoresis in animal models: a randomized experimental study
Abstract
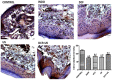
The aim of this study was to evaluate the therapeutic effects of ultrasound (US)-mediated phonophoresis alone or in association with diclofenac diethylammonium (DCF) administered topically in animal models of inflammation. A pre-clinical, prospective, and randomized experimental study of quantitative and qualitative nature was carried out. Phonophoresis was performed using a therapeutic ultrasound apparatus in two distinct models of acute inflammation. Edema was induced by an intraplantar injection of carrageenan and measured by plethysmography. The Hargreaves test was used to evaluate the antinociceptive activity and investigate the action of phonophoresis on tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α production. A histological analysis with hematoxylin-eosin was used to evaluate tissue repair, and the expression of COX-2 was determined by immunohistochemical analysis. At the peak of inflammatory activity (3 h), treatment with US, US+DCF, and DCF significantly reduced edema formation compared to the control group. Treatment with US+DCF was more effective than treatment with US alone at both analyzed times. In the analysis of the antinociceptive activity, the treatments significantly increased the latency time in response to the thermal stimulus. Histopathological analysis revealed a reduction of the inflammatory infiltrates and immunohistochemistry demonstrated that the association was effective in reducing COX-2 expression compared to the control group. The association of DCF with US produced anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects in rat models of inflammation, which may be associated with inhibition of COX-2 and TNF-α production.
Figures

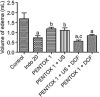


Similar articles
-
Effects of ultrasound and diclofenac phonophoresis on inflammatory pain relief: suppression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in arthritic rats.Phys Ther. 2006 Jan;86(1):39-49. doi: 10.1093/ptj/86.1.39. Phys Ther. 2006. PMID: 16386061
-
Comparative study of the topical application of Aloe vera gel, therapeutic ultrasound and phonophoresis on the tissue repair in collagenase-induced rat tendinitis.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2010 Oct;36(10):1682-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2010.06.012. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20800944
-
Inflammatory cytokines content in Achilles tendinopathy after phonophoresis treatment combined with gold nanoparticles and diclophenac diethylammonium in rats.Inflammation. 2015;38(3):1044-9. doi: 10.1007/s10753-014-0069-x. Inflammation. 2015. PMID: 25428204
-
Evaluation of factors influencing the quality and efficacy of ultrasound and phonophoresis treatment.Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2007 Sep-Oct;9(5):449-58. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2007. PMID: 18026065 Review.
-
Central antinociceptive effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and paracetamol. Experimental studies in the rat.Acta Anaesthesiol Scand Suppl. 1995;103:1-44. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand Suppl. 1995. PMID: 7725891 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Utility of Ultrasound-Enhanced Delivery of Antibiotics, Anti-Inflammatory Agents, and Nutraceuticals: A Mini Review.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Sep 22;11(10):1290. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11101290. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36289948 Free PMC article.
-
Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound phonophoresis with diclofenac alleviated inflammation and pain via downregulation of M1 macrophages in rats with carrageenan-induced knee joint arthritis.Neurobiol Pain. 2023 Dec 6;15:100148. doi: 10.1016/j.ynpai.2023.100148. eCollection 2024 Jan-Jun. Neurobiol Pain. 2023. PMID: 38174056 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oliveira AS, Guaratini MI, Castro CES. A iontoforese na prática fisioterapêutica. Fisio Bras. 2007;8:430–435.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

