New de novo assembly of the Atlantic bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) improves genome completeness and provides haplotype phasing
- PMID: 30698692
- PMCID: PMC6443575
- DOI: 10.1093/gigascience/giy168
New de novo assembly of the Atlantic bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) improves genome completeness and provides haplotype phasing
Abstract
High-quality genomes are essential to resolve challenges in breeding, comparative biology, medicine, and conservation planning. New library preparation techniques along with better assembly algorithms result in continued improvements in assemblies for non-model organisms, moving them toward reference-quality genomes. We report on the latest genome assembly of the Atlantic bottlenose dolphin, leveraging Illumina sequencing data coupled with a combination of several library preparation techniques. These include Linked-Reads (Chromium, 10x Genomics), mate pairs (MP), long insert paired ends, and standard paired end. Data were assembled with the commercial DeNovoMAGIC assembly software, resulting in two assemblies, a traditional "haploid" assembly (Tur_tru_Illumina_hap_v1) that is a mosaic of the two parental haplotypes and a phased assembly (Tur_tru_Illumina_phased_v1) where each scaffold has sequence from a single homologous chromosome. We show that Tur_tru_Illumina_hap_v1 is more complete and more accurate compared to the current best reference based on the amount and composition of sequence, the consistency of the MP alignments to the assembled scaffolds, and on the analysis of conserved single-copy mammalian orthologs. The phased de novo assembly Tur_tru_Illumina_phased_v1 is the first publicly available for this species and provides the community with novel and accurate ways to explore the heterozygous nature of the dolphin genome.
Keywords: Tursiops truncatus; de novo genome assembly; 10x Genomics; DeNovoMAGIC; Illumina; bottlenose dolphin.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
K.V. and C.T.L. were both full-time employees of Illumina at the time this work was completed. G.B.Z., K.B., and T.B. are employees of NRGene, a company that provides software analysis tools for
Figures
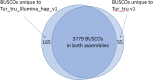

Similar articles
-
Proteomics as a Metrological Tool to Evaluate Genome Annotation Accuracy Following De Novo Genome Assembly: A Case Study Using the Atlantic Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops truncatus).Genes (Basel). 2023 Aug 25;14(9):1696. doi: 10.3390/genes14091696. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37761836 Free PMC article.
-
De novo assembly and phasing of a Korean human genome.Nature. 2016 Oct 13;538(7624):243-247. doi: 10.1038/nature20098. Epub 2016 Oct 5. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27706134
-
Assembly of complete diploid-phased chromosomes from draft genome sequences.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Jul 29;12(8):jkac143. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac143. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 35686922 Free PMC article.
-
The Gulf of Ambracia's Common Bottlenose Dolphins, Tursiops truncatus: A Highly Dense and yet Threatened Population.Adv Mar Biol. 2016;75:259-296. doi: 10.1016/bs.amb.2016.07.002. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Adv Mar Biol. 2016. PMID: 27770987 Review.
-
De novo phasing resolves haplotype sequences in complex plant genomes.Plant Biotechnol J. 2022 Jun;20(6):1031-1041. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13815. Epub 2022 Apr 9. Plant Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 35332665 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Taro Genome Assembly and Linkage Map Reveal QTLs for Resistance to Taro Leaf Blight.G3 (Bethesda). 2020 Aug 5;10(8):2763-2775. doi: 10.1534/g3.120.401367. G3 (Bethesda). 2020. PMID: 32546503 Free PMC article.
-
Selection of a reference gene for studies on lipid-related aquatic adaptations of toothed whales (Grampus griseus).Ecol Evol. 2021 Nov 26;11(23):17142-17159. doi: 10.1002/ece3.8354. eCollection 2021 Dec. Ecol Evol. 2021. PMID: 34938499 Free PMC article.
-
Gene duplications and gene loss in the epidermal differentiation complex during the evolutionary land-to-water transition of cetaceans.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 10;11(1):12334. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91863-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34112911 Free PMC article.
-
Production of WW males lacking the masculine Z chromosome and mining the Macrobrachium rosenbergii genome for sex-chromosomes.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 27;9(1):12408. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-47509-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31455815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avni R, Nave M, Barad O, et al. .. Wild emmer genome architecture and diversity elucidate wheat evolution and domestication. Science. 2017;357(6346):93–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

