Synthesis and Preliminary Evaluations of a Triazole-Cored Antagonist as a PET Imaging Probe ([18F]N2B-0518) for GluN2B Subunit in the Brain
- PMID: 30698943
- PMCID: PMC6727982
- DOI: 10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00591
Synthesis and Preliminary Evaluations of a Triazole-Cored Antagonist as a PET Imaging Probe ([18F]N2B-0518) for GluN2B Subunit in the Brain
Abstract
GluN2B is the most studied subunit of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) and implicated in the pathologies of various central nervous system disorders and neurodegenerative diseases. As pan NMDAR antagonists often produce debilitating side effects, new approaches in drug discovery have shifted to subtype-selective NMDAR modulators, especially GluN2B-selective antagonists. While positron emission tomography (PET) studies of GluN2B-selective NMDARs in the living brain would enable target engagement in drug development and improve our understanding in the NMDAR signaling pathways between normal and disease conditions, a suitable PET ligand is yet to be identified. Herein we developed an 18F-labeled potent antagonist, 2-((1-(4-[18F]fluoro-3-methylphenyl)-1 H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methoxy)-5-methoxypyrimidine ([18F]13; also called [18F]N2B-0518) as a PET tracer for imaging the GluN2B subunit. The radiofluorination of [18F]13 was efficiently achieved by our spirocyclic iodonium ylide (SCIDY) method. In in vitro autoradiography studies, [18F]13 displayed highly region-specific binding in brain sections of rat and nonhuman primate, which was in accordance with the expression of GluN2B subunit. Ex vivo biodistribution in mice revealed that [18F]13 could penetrate the blood-brain barrier with moderate brain uptake (3.60% ID/g at 2 min) and rapid washout. Altogether, this work provides a GluN2B-selective PET tracer bearing a new chemical scaffold and shows high specificity to GluN2B subunit in vitro, which may pave the way for the development of a new generation of GluN2B PET ligands.
Keywords: 18F-labeling; GluN2B subunit; PET imaging; Subtype-selective; autoradiography; spirocyclic iodonium ylide.
Figures
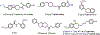


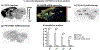


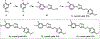
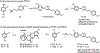
References
-
- Paoletti P, Bellone C, and Zhou Q (2013) NMDA receptor subunit diversity: impact on receptor properties, synaptic plasticity and disease, Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 14, 383–400. - PubMed
-
- Parsons MP, and Raymond LA (2014) Extrasynaptic NMDA receptor involvement in central nervous system disorders, Neuron 82, 279–293. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez J, Jurado-Coronel JC, Avila MF, Sabogal A, Capani F, and Barreto GE (2015) NMDARs in neurological diseases: a potential therapeutic target, Int. J. Neurosci. 125, 315–327. - PubMed
-
- Chazot PL (2004) The NMDA receptor NR2B subunit: a valid therapeutic target for multiple CNS pathologies, Curr. Med. Chem. 11, 389–396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

