Islet-cell autoantigen 69 mediates the antihyperalgesic effects of electroacupuncture on inflammatory pain by regulating spinal glutamate receptor subunit 2 phosphorylation through protein interacting with C-kinase 1 in mice
- PMID: 30699097
- PMCID: PMC6407810
- DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001450
Islet-cell autoantigen 69 mediates the antihyperalgesic effects of electroacupuncture on inflammatory pain by regulating spinal glutamate receptor subunit 2 phosphorylation through protein interacting with C-kinase 1 in mice
Abstract
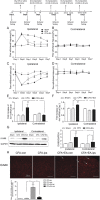
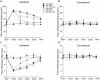
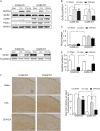
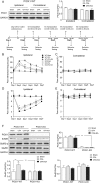
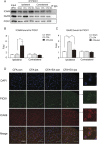
Electroacupuncture (EA) is widely used in clinical settings to reduce inflammatory pain. Islet-cell autoantigen 69 (ICA69) has been reported to regulate long-lasting hyperalgesia in mice. ICA69 knockout led to reduced protein interacting with C-kinase 1 (PICK1) expression and increased glutamate receptor subunit 2 (GluR2) phosphorylation at Ser880 in spinal dorsal horn. In this study, we evaluated the role of ICA69 in the antihyperalgesic effects of EA and the underlying mechanism through regulation of GluR2 and PICK1 in spinal dorsal horn. Hyperalgesia was induced in mice with subcutaneous plantar injection of complete Freund adjuvant (CFA) to cause inflammatory pain. Electroacupuncture was then applied for 30 minutes every other day after CFA injection. When compared with CFA group, paw withdrawal frequency of CFA+EA group was significantly decreased. Remarkable increases in Ica1 mRNA expression and ICA69 protein levels on the ipsilateral side were detected in the CFA+EA group. ICA69 expression reached the peak value around day 3. More importantly, ICA69 deletion impaired the antihyperalgesic effects of EA on GluR2-p, but PICK1 deletion could not. Injecting ICA69 peptide into the intrathecal space of ICA69-knockout mice mimicked the effects of EA analgesic and inhibited GluR2-p. Electroacupuncture had no effects on the total protein of PICK1 and GluR2. And, EA could increase the formation of ICA69-PICK1 complexes and decrease the amount of PICK1-GluR2 complexes. Our findings indicate that ICA69 mediates the antihyperalgesic effects of EA on CFA-induced inflammatory pain by regulating spinal GluR2 through PICK1 in mice.
Conflict of interest statement
Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Aoyama K, Matsumura N, Watabe M, Nakaki T. Oxidative stress on EAAC1 is involved in MPTP-induced glutathione depletion and motor dysfunction. Eur J Neurosci 2008;27:20–30. - PubMed
-
- Atianjoh FE, Yaster M, Zhao X, Takamiya K, Xia J, Gauda EB, Huganir RL, Tao YX. Spinal cord protein interacting with C kinase 1 is required for the maintenance of complete Freund's adjuvant-induced inflammatory pain but not for incision-induced post-operative pain. PAIN 2010;151:226–34. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barnes PM, Barbara B, Nahin RL. Complementary and alternative medicine use among adults and children: United States, 2007. Natl Health Stat Rep 2008;12:1–23. - PubMed
-
- Berman BM, Lao L, Langenberg P, Lee WL, Gilpin AM, Hochberg MC. Effectiveness of acupuncture as adjunctive therapy in osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 2004;141:901–10. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

