Targeting Hedgehog Signalling through the Ubiquitylation Process: The Multiple Roles of the HECT-E3 Ligase Itch
- PMID: 30699938
- PMCID: PMC6407099
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8020098
Targeting Hedgehog Signalling through the Ubiquitylation Process: The Multiple Roles of the HECT-E3 Ligase Itch
Abstract
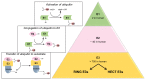
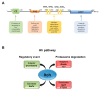
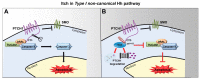
Hedgehog signalling (Hh) is a developmental conserved pathway strongly involved in cancers when deregulated. This important pathway is orchestrated by numerous regulators, transduces through distinct routes and is finely tuned at multiple levels. In this regard, ubiquitylation processes stand as essential for controlling Hh pathway output. Although this post-translational modification governs proteins turnover, it is also implicated in non-proteolytic events, thereby regulating the most important cellular functions. The HECT E3 ligase Itch, well known to control immune response, is emerging to have a pivotal role in tumorigenesis. By illustrating Itch specificities on Hh signalling key components, here we review the role of this HECT E3 ubiquitin ligase in suppressing Hh-dependent tumours and explore its potential as promising target for innovative therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: GLI1; Hedgehog; Itch; Numb; Patched1; SuFu; cancer; ubiquitylation; β-arrestin2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Itch/β-arrestin2-dependent non-proteolytic ubiquitylation of SuFu controls Hedgehog signalling and medulloblastoma tumorigenesis.Nat Commun. 2018 Mar 7;9(1):976. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03339-0. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29515120 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog/Gli control by ubiquitination/acetylation interplay.Vitam Horm. 2012;88:211-27. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394622-5.00009-2. Vitam Horm. 2012. PMID: 22391305 Review.
-
Multiple ubiquitin-dependent processing pathways regulate hedgehog/gli signaling: implications for cell development and tumorigenesis.Cell Cycle. 2007 Feb 15;6(4):390-3. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.4.3809. Epub 2007 Feb 3. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17312394
-
MEP50/PRMT5-mediated methylation activates GLI1 in Hedgehog signalling through inhibition of ubiquitination by the ITCH/NUMB complex.Commun Biol. 2019 Jan 18;2:23. doi: 10.1038/s42003-018-0275-4. eCollection 2019. Commun Biol. 2019. PMID: 30675521 Free PMC article.
-
The E3 ligase Itch in immune regulation and beyond.Immunol Rev. 2015 Jul;266(1):6-26. doi: 10.1111/imr.12301. Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26085204 Review.
Cited by
-
The Roles of NEDD4 Subfamily of HECT E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Neurodevelopment and Neurodegeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 31;23(7):3882. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073882. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The regulatory roles of the E3 ubiquitin ligase NEDD4 family in DNA damage response.Front Physiol. 2022 Aug 26;13:968927. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.968927. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36091384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitin Ligases Involved in the Regulation of Wnt, TGF-β, and Notch Signaling Pathways and Their Roles in Mouse Development and Homeostasis.Genes (Basel). 2019 Oct 16;10(10):815. doi: 10.3390/genes10100815. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31623112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteolysis-Targeting Chimera (PROTAC): Is the Technology Looking at the Treatment of Brain Tumors?Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 15;10:854352. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.854352. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35242765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of Notch pathway components (Numb, Itch, and Siah-1) in colorectal tumors: A clinicopathological study.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Jul 14;26(26):3814-3833. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i26.3814. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32774060 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schüller U., Heine V.M., Mao J., Kho A.T., Dillon A.K., Han Y.G., Huillard E., Sun T., Ligon A.H., Qian Y., et al. Acquisition of granule neuron precursor identity is a critical determinant of progenitor cell competence to form Shh-induced medulloblastoma. Cancer Cell. 2008;14:123–134. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.07.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang Z.J., Ellis T., Markant S.L., Read T.A., Kessler J.D., Bourboulas M., Schüller U., Machold R., Fishell G., Rowitch D.H., et al. Medulloblastoma can be initiated by deletion of Patched in lineage-restricted progenitors or stem cells. Cancer Cell. 2008;14:135–145. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.07.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

