Advances of Non-Ionic Surfactant Vesicles (Niosomes) and Their Application in Drug Delivery
- PMID: 30700021
- PMCID: PMC6410054
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11020055
Advances of Non-Ionic Surfactant Vesicles (Niosomes) and Their Application in Drug Delivery
Abstract
Non-Ionic surfactant based vesicles, also known as niosomes, have attracted much attention in pharmaceutical fields due to their excellent behavior in encapsulating both hydrophilic and hydrophobic agents. In recent years, it has been discovered that these vesicles can improve the bioavailability of drugs, and may function as a new strategy for delivering several typical of therapeutic agents, such as chemical drugs, protein drugs and gene materials with low toxicity and desired targeting efficiency. Compared with liposomes, niosomes are much more stable during the formulation process and storage. The required pharmacokinetic properties can be achieved by optimizing components or by surface modification. This novel delivery system is also easy to prepare and scale up with low production costs. In this paper, we summarize the structure, components, formulation methods, quality control of niosome and its applications in chemical drugs, protein drugs and gene delivery.
Keywords: carrier; drug delivery; niosome; non-ionic surfactant; stability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


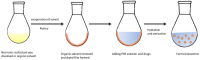
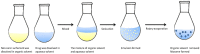
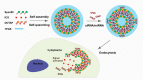

References
-
- Ravi M.K. Nano and microparticles as controlled drug delivery devices. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2000;3:234. - PubMed
-
- Sahoo S.K., Jain T.K., Reddy M.K., Labhasetwar V. Nano-Sized Carriers for Drug Delivery. Nanobiotechnology. 2008:329–348. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-218-2_13. - DOI
-
- Malipeddi V.R., Dua K., Pinto T.D.J.A., Kikuchi I.S., Kulkarni G.T., Pant I., Awasthi R. Opportunities and Challenges in Nano-structure Mediated Drug Delivery: Where Do We Stand? Curr. Nanomed. 2016;6:78–104.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

