Prognostic Hemostasis Biomarkers in Acute Ischemic Stroke
- PMID: 30700129
- PMCID: PMC6392207
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.312102
Prognostic Hemostasis Biomarkers in Acute Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
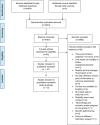
Objectives- The prediction of patients at risk for poor clinical outcome after acute ischemic stroke remains challenging. An imbalance of coagulation factors may play an important role in progression and prognosis of these patients. In this systematic review, we assessed the current literature on hemostasis biomarkers and the association with poor clinical outcome in acute ischemic stroke. Approach and Results- A systematic search of Embase, Medline, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, and Google Scholar was performed on studies reporting on hemostasis biomarkers and clinical outcome after acute ischemic stroke. Studies were considered eligible if blood samples were collected within 72 hours after symptom onset. Additionally, clinical outcome should be assessed using a disability score (Barthel Index or modified Rankin scale). Methodological quality of included studies was assessed with an adapted version of the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies questionnaire. A total of 80 articles were read full text, and 41 studies were considered eligible for inclusion, reporting on 37 different hemostasis biomarkers. No single biomarker appeared to be effective in predicting poor clinical outcome in acute ischemic stroke patients. Conclusions- Based on current literature, no clear recommendations can be provided on which hemostasis biomarkers are a predictor of clinical outcome after acute ischemic stroke. However, some biomarkers show promising results and need to be further investigated and validated in large populations with clear defined study designs.
Keywords: biomarkers; brain ischemic; hemostasis; prognosis; systematic review.
Figures
References
-
- Folsom AR, Rosamond WD, Shahar E, Cooper LS, Aleksic N, Nieto FJ, Rasmussen ML, Wu KK. Prospective study of markers of hemostatic function with risk of ischemic stroke. The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study Investigators. Circulation. 1999;100:736–742. - PubMed
-
- Sonneveld MA, de Maat MP, Portegies ML, Kavousi M, Hofman A, Turecek PL, Rottensteiner H, Scheiflinger F, Koudstaal PJ, Ikram MA, Leebeek FW. Low ADAMTS13 activity is associated with an increased risk of ischemic stroke. Blood. 2015;126:2739–2746. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-05-643338. - PubMed
-
- van Schie MC, DE Maat MP, Dippel DW, de Groot PG, Lenting PJ, Leebeek FW, Hollestelle MJ. von Willebrand factor propeptide and the occurrence of a first ischemic stroke. J Thromb Haemost. 2010;8:1424–1426. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.03863.x. - PubMed
-
- Tzoulaki I, Murray GD, Lee AJ, Rumley A, Lowe GD, Fowkes FG. Relative value of inflammatory, hemostatic, and rheological factors for incident myocardial infarction and stroke: the Edinburgh Artery Study. Circulation. 2007;115:2119–2127. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.635029. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources