Postpartum blood pressure patterns in severe preeclampsia and normotensive pregnant women following abdominal deliveries: a cohort study
- PMID: 30700189
- PMCID: PMC7193714
- DOI: 10.1080/14767058.2019.1569621
Postpartum blood pressure patterns in severe preeclampsia and normotensive pregnant women following abdominal deliveries: a cohort study
Abstract
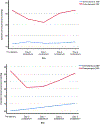
Objective: To determine blood pressure (BP) patterns in the immediate postpartum period in preeclampsia with severe features (sPE) and normotensive pregnant women who had cesarean deliveries (CD).Study design: The BP levels of two groups comprising 50 sPE and 90 normotensive pregnant women who had CD were measured before delivery and on days 0-3 postpartum at four time points (05:00, 08:00, 14:00, and 22:00). Soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (sFlt-1) and placental growth factor (PIGF) were measured in the maternal serum ≤48 h before delivery.Results: Antihypertensive therapy was administered to 98, 96, 82, 78, and 56% of sPE antepartum and on postpartum days 0-3, respectively. De novo postpartum hypertension (BP ≥ 140/90 mmHg) occurred in 24.4% (22/90) of the normotensive group but only one required antihypertensive therapy. The occurrence of de novo postpartum hypertension was associated with maternal weight before delivery ≥ 84.5 kg (relative risks (RR) 2.6, CI 95% 1.2-5.8, p = .017), and body mass index before delivery ≥ 33.3 kg/m2 (RR 2.9, CI 95% 1.3-6.4, p = .008). In sPE, the BP decreased between predelivery period and postpartum day 0. From days 1 to 3 postpartum, there was a continuous increase in the daily mean BPs in both groups, with average daily increments (systolic/diastolic) being 5.6/4.6 mmHg and 0.6/1.3 mmHg in the sPE and normotensive women, respectively. Patient's group and time had a significant effect on BP, p < .001. Overall, daily mean BPs were higher in the sPE than the normotensive group (p < .001). Perceived stress (p = .022), low birth weight (p = .002), 5 min Apgar score ≤ 6 (p < .001) were significantly higher in the sPE group. sFlt-1/PIGF ratio was high in the hypertensive groups: sPE versus normotensive group, p < .001; de novo postpartum hypertension versus normotensives group that remained normotensive, p = .102.Conclusion: Postpartum BP and antihypertensive requirements are important considerations in managing sPE and normotensive pregnancies. sPE is associated with increased maternal stress and poor perinatal outcomes.
Keywords: Caesarean delivery; perceived stress scale; perinatal outcomes; postpartum hypertension; preeclampsia with severe features.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The performance of pre-delivery serum concentrations of angiogenic factors in predicting postpartum antihypertensive drug therapy following abdominal delivery in severe preeclampsia and normotensive pregnancy.PLoS One. 2019 Apr 25;14(4):e0215807. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215807. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31022243 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-delivery angiogenic factors and their association with peripartum perceived stress and pain in pre-eclampsia with severe features and normotensive pregnancies.Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2022 Aug;158(2):398-405. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.13972. Epub 2021 Oct 31. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2022. PMID: 34622454 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology and Mechanisms of De Novo and Persistent Hypertension in the Postpartum Period.Circulation. 2015 Nov 3;132(18):1726-33. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.015721. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Circulation. 2015. PMID: 26416810 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of intra-abdominal hypertension on maternal-fetal outcomes in term pregnant women: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2023 Jun 27;18(6):e0280869. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280869. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37368887 Free PMC article.
-
[Application of the concetrations ratio of soluble receptor tyrosine kinase type 1, and placental growth factor for short-term prediction and diagnosis of preeclampsia].Ceska Gynekol. 2016 Summer;81(4):272-278. Ceska Gynekol. 2016. PMID: 27882748 Review. Czech.
Cited by
-
The performance of pre-delivery serum concentrations of angiogenic factors in predicting postpartum antihypertensive drug therapy following abdominal delivery in severe preeclampsia and normotensive pregnancy.PLoS One. 2019 Apr 25;14(4):e0215807. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215807. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31022243 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-eclampsia with severe features: management of antihypertensive therapy in the postpartum period.Pan Afr Med J. 2020 Jul 27;36:216. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2020.36.216.19895. eCollection 2020. Pan Afr Med J. 2020. PMID: 32963682 Free PMC article.
-
Mode of delivery in placental abruption: A case report on difficulty in distinguishing between uterine rupture and placental abruption due to clinical features that overlap.Case Rep Womens Health. 2025 May 15;46:e00715. doi: 10.1016/j.crwh.2025.e00715. eCollection 2025 Jun. Case Rep Womens Health. 2025. PMID: 40486903 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Recurrent Preeclampsia and Attendance at the Blood Pressure Monitoring Appointment After Birth.J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. 2024 Mar;53(2):132-139. doi: 10.1016/j.jogn.2023.11.002. Epub 2023 Nov 22. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38006903 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. World health statistics 2016: monitoring health for the SDGs, sustainable development goals. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2016.
-
- National Committee on the Confidential Enquiries into Maternal Deaths. Saving Mothers 2014–2016: Seventh triennial report on confidential enquiries into maternal deaths in South Africa: Short report. Pretoria: South African Department of Health 2018.
-
- Granger JP, LaMarca BB, Cockrell K, et al. Reduced uterine perfusion pressure (RUPP) model for studying cardiovascular-renal dysfunctionin response to placental ischemia. Methods Mol Med 2006;122:383–392. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous