Comparative effects of lipid lowering, hypoglycemic, antihypertensive and antiplatelet medications on carotid artery intima-media thickness progression: a network meta-analysis
- PMID: 30700294
- PMCID: PMC6352423
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-019-0817-1
Comparative effects of lipid lowering, hypoglycemic, antihypertensive and antiplatelet medications on carotid artery intima-media thickness progression: a network meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Carotid artery intima-media thickness (cIMT) progression is a surrogate marker of atherosclerosis with a high predictive value for future CVD risk. This study evaluates the comparative efficacies of lipid lowering, hypoglycemic, antihypertensive and antiplatelet medications on cIMT progression.
Methods: We conducted a network meta-analysis (NMA) to evaluate the relative efficacies of several drug classes in modifying cIMT progression. After a literature search in several electronic databases, studies were selected by following predetermined eligibility criteria. An inverse variance-heterogeneity model was used for NMA. Sensitivity analyses were performed to check the reliability of the overall NMA, and transitivity analyses were performed to examine the effects of modifiers on the NMA outcomes.
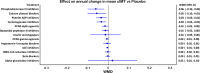
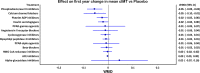
Results: Data were taken from 47 studies (15,721 patients; age: 60.2 years [95% confidence interval (CI) 58.8, 61.6]; BMI: 27.2 kg/m2 [95% CI 26.4, 28.0]; and gender: 58.3% males [95% CI 48.3, 68.3]). Treatment duration was 25.8 months [95% CI 22.9, 28.7]. Of the 13 drug classes in the network, treatment with phosphodiesterase III inhibitors was the most effective in retarding annual mean cIMT against network placebo (weighted mean difference (WMD) - 0.059 mm [95% CI - 0.099, - 0.020) followed by the calcium channel blockers (WMD - 0.055 mm [95% CI - 0.099, 0.001]) and platelet adenosine diphosphate inhibitors (WMD - 0.033 mm [95% CI - 0.058, 0.008]). These 3 drug classes also attained the same positions when the NMA was conducted by using first-year changes in mean cIMT. In transitivity analyses, longer treatment duration, higher body mass index (BMI), and a higher baseline cIMT were found to be independently associated with a lesser reduction in annual mean cIMT. However, in a multivariate analysis with these 3 modifiers, none of these factors was significantly associated with annual change in mean cIMT. In the placebo group, age was inversely associated with annual change in mean cIMT independently.
Conclusion: Phosphodiesterase III inhibitors and calcium channel blockers are found more effective than other drug classes in retarding cIMT progression. Age, BMI, and baseline cIMT may have some impact on these outcomes.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Cardiovascular; Diabetes; Intima-media thickness; Metabolic disorders.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Sleeve Gastrectomy and Gastric Bypass Decrease the Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Obese Men: Association with Weight Loss, Cardiovascular Risk Factors, and Circulating Testosterone.Obes Surg. 2020 Mar;30(3):851-859. doi: 10.1007/s11695-020-04405-7. Obes Surg. 2020. PMID: 31925727 Clinical Trial.
-
Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Progression as Surrogate Marker for Cardiovascular Risk: Meta-Analysis of 119 Clinical Trials Involving 100 667 Patients.Circulation. 2020 Aug 18;142(7):621-642. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.046361. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Circulation. 2020. PMID: 32546049 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of aspirin in patients with established asymptomatic carotid atherosclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 7;13:1041400. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1041400. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36569309 Free PMC article.
-
Association between small dense low-density lipoprotein and carotid intima-media thickness.J Cardiovasc Thorac Res. 2024;16(4):202-210. doi: 10.34172/jcvtr.33145. Epub 2024 Dec 23. J Cardiovasc Thorac Res. 2024. PMID: 40027367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovering Inflammation in Atherosclerosis: Insights from Pathogenic Pathways to Clinical Practice.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 30;25(11):6016. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116016. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892201 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lorenz MW, Polak JF, Kavousi M, Mathiesen EB, Völzke H, Tuomainen TP, et al. Carotid intima-media thickness progression to predict cardiovascular events in the general population (the PROG-IMT collaborative project): a meta-analysis of individual participant data. Lancet. 2012;379(9831):2053–2062. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60441-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

