Handheld ECG Tracking of in-hOspital Atrial Fibrillation The HECTO-AF trial Clinical Study Protocol
- PMID: 30700332
- PMCID: PMC6354419
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-019-3189-7
Handheld ECG Tracking of in-hOspital Atrial Fibrillation The HECTO-AF trial Clinical Study Protocol
Abstract
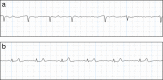
Background/rationale: Atrial fibrillation (AF) is frequent and causes great morbidity in the aging population. While initial events may be symptomatic, many patients have silent AF and are at risk of ischemic embolic complications. Timely detection of asymptomatic patients is paramount. The HECTO-AF trial aims to investigate the efficacy of an electrocardiogram (ECG) handheld device for the detection of AF in patients in hospital without a prior diagnosis of AF.
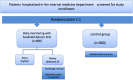
Methods/design: The "Handheld ECG tracking of in-hospital atrial fibrillation" (HECTO-AF) study is a single-center, open-label, randomized controlled trial. The study population consists of all adult patients admitted to a general medicine ward of the University and Hospital of Fribourg throughout the study period. The study will enroll 1600 patients with 1:1 ratio allocation to either the detection group with one-lead handheld ECG recordings twice daily and extra recordings in the case of palpitations, versus a control group undergoing detection of AF as per routine clinical practice. Recordings will be self-performed after dedicated training, and will be independently adjudicated through a specific web-based interface. All enrolled patients will be followed clinically at 1, 2 and 5 years to assess the occurrence of AF, death, non-fatal stroke, systemic embolism, myocardial infarction and bleeding. The primary outcome is incidence of newly detected AF during the hospital stay. Secondary outcomes are incidence of AF, cardiovascular death, stroke, myocardial infarction and bleeding complications at 1, 2 and 5 years.
Discussion: HECTO-AF is an independent randomized study aiming to detect the incidence of silent AF in all-comers hospitalized in general medicine wards.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT03197090 . Registered on 23 June 2017. Local ethical Committee (CER-VD) registration number: 2017-01594. There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Atrial fibrillation screening; ECG handheld device; General medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the local ethics committee of Vaud (Switzerland, CER-VD 2017–01594).
Consent for publication
All authors consented to publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Handheld ECG Tracking of in-hOspital Atrial Fibrillation (HECTO-AF): A Randomized Controlled Trial.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 May 4;8:681890. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.681890. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34017869 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of handheld electrocardiogram devices to detect atrial fibrillation in a cardiology and geriatric ward setting.Europace. 2017 Jan;19(1):29-39. doi: 10.1093/europace/euw025. Epub 2016 Feb 17. Europace. 2017. PMID: 26893496
-
Assessment of Remote Heart Rhythm Sampling Using the AliveCor Heart Monitor to Screen for Atrial Fibrillation: The REHEARSE-AF Study.Circulation. 2017 Nov 7;136(19):1784-1794. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.030583. Epub 2017 Aug 28. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 28851729 Clinical Trial.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of handheld electrocardiogram devices in detecting atrial fibrillation in adults in community versus hospital settings: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Heart. 2020 Aug;106(16):1211-1217. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2020-316611. Epub 2020 May 11. Heart. 2020. PMID: 32393588
-
[Screening and clinical implications of silent atrial fibrillation].Rev Med Interne. 2018 Jul;39(7):574-579. doi: 10.1016/j.revmed.2017.08.006. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Rev Med Interne. 2018. PMID: 28942937 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Feasibility and Reliability of SmartWatch to Obtain 3-Lead Electrocardiogram Recordings.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Sep 7;20(18):5074. doi: 10.3390/s20185074. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32906661 Free PMC article.
-
Handheld ECG Tracking of in-hOspital Atrial Fibrillation (HECTO-AF): A Randomized Controlled Trial.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 May 4;8:681890. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.681890. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34017869 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

