NDM Metallo-β-Lactamases and Their Bacterial Producers in Health Care Settings
- PMID: 30700432
- PMCID: PMC6431124
- DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00115-18
NDM Metallo-β-Lactamases and Their Bacterial Producers in Health Care Settings
Abstract
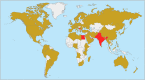
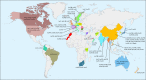
New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase (NDM) is a metallo-β-lactamase able to hydrolyze almost all β-lactams. Twenty-four NDM variants have been identified in >60 species of 11 bacterial families, and several variants have enhanced carbapenemase activity. Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli are the predominant carriers of blaNDM, with certain sequence types (STs) (for K. pneumoniae, ST11, ST14, ST15, or ST147; for E. coli, ST167, ST410, or ST617) being the most prevalent. NDM-positive strains have been identified worldwide, with the highest prevalence in the Indian subcontinent, the Middle East, and the Balkans. Most blaNDM-carrying plasmids belong to limited replicon types (IncX3, IncFII, or IncC). Commonly used phenotypic tests cannot specifically identify NDM. Lateral flow immunoassays specifically detect NDM, and molecular approaches remain the reference methods for detecting blaNDM Polymyxins combined with other agents remain the mainstream options of antimicrobial treatment. Compounds able to inhibit NDM have been found, but none have been approved for clinical use. Outbreaks caused by NDM-positive strains have been reported worldwide, attributable to sources such as contaminated devices. Evidence-based guidelines on prevention and control of carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria are available, although none are specific for NDM-positive strains. NDM will remain a severe challenge in health care settings, and more studies on appropriate countermeasures are required.
Keywords: Acinetobacter; Enterobacteriaceae; NDM; carbapenem resistance; carbapenemase; metalloenzymes.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures


References
-
- Yong D, Toleman MA, Giske CG, Cho HS, Sundman K, Lee K, Walsh TR. 2009. Characterization of a new metallo-β-lactamase gene, blaNDM-1, and a novel erythromycin esterase gene carried on a unique genetic structure in Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 14 from India. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53:5046–5054. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00774-09. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

