Disseminated intestinal basidiobolomycosis with mycotic aneurysm mimicking obstructing colon cancer
- PMID: 30700449
- PMCID: PMC6352788
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2018-225054
Disseminated intestinal basidiobolomycosis with mycotic aneurysm mimicking obstructing colon cancer
Abstract
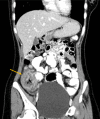
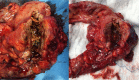
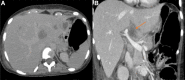
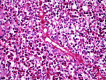
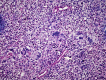
Basidiobolomycosis is a rare fungal infection that may affect the gastrointestinal tract. It is caused by Basidiobolus ranarum and less than 80 cases have been reported in the literature. The incidence seems to be higher in the Middle East and in particular Saudi Arabia where most cases are diagnosed in the south-western region. An 18-year-old woman presented to the emergency department with an obstructing caecal mass initially suspected to be malignant. Surgical resection was complicated by bowel perforation, histology and cultures confirmed basidiobolomycosis infection. The postoperative course was complicated by an enterocutaneous fistula, fungal intra-abdominal abscesses, liver and lung abscesses, formation of mycotic hepatic artery aneurysm and meningoencephalitis. The patient eventually expired due to sepsis despite aggressive treatment. Diagnosis and management of such rare cases are very challenging and require a multidisciplinary approach. Complications are common and associated with a high mortality.
Keywords: gastrointestinal surgery; gastrointestinal system; general surgery; infections; liver disease.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
