Deubiquitinating enzyme USP30 maintains basal peroxisome abundance by regulating pexophagy
- PMID: 30700497
- PMCID: PMC6400567
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201804172
Deubiquitinating enzyme USP30 maintains basal peroxisome abundance by regulating pexophagy
Abstract
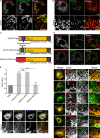
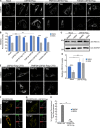
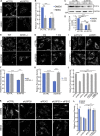
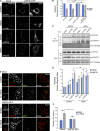
The regulation of organelle abundance is critical for cell function and survival; however, the mechanisms responsible are not fully understood. In this study, we characterize a role of the deubiquitinating enzyme USP30 in peroxisome maintenance. Peroxisomes are highly dynamic, changing in abundance in response to metabolic stress. In our recent study identifying the role of USP30 in mitophagy, we observed USP30 to be localized to punctate structures resembling peroxisomes. We report here that USP30, best known as a mitophagy regulator, is also necessary for regulating pexophagy, the selective autophagic degradation of peroxisomes. We find that overexpressing USP30 prevents pexophagy during amino acid starvation, and its depletion results in pexophagy induction under basal conditions. We demonstrate that USP30 prevents pexophagy by counteracting the action of the peroxisomal E3 ubiquitin ligase PEX2. Finally, we show that USP30 can rescue the peroxisome loss observed in some disease-causing peroxisome mutations, pointing to a potential therapeutic target.
© 2019 Riccio et al.
Figures
Comment in
-
New aspects of USP30 biology in the regulation of pexophagy.Autophagy. 2019 Sep;15(9):1634-1637. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1615304. Epub 2019 Jun 9. Autophagy. 2019. PMID: 31356149 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braverman N.E., Raymond G.V., Rizzo W.B., Moser A.B., Wilkinson M.E., Stone E.M., Steinberg S.J., Wangler M.F., Rush E.T., Hacia J.G., and Bose M.. 2016. Peroxisome biogenesis disorders in the Zellweger spectrum: An overview of current diagnosis, clinical manifestations, and treatment guidelines. Mol. Genet. Metab. 117:313–321. 10.1016/j.ymgme.2015.12.009 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

