The ORMDL/Orm-serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT) complex is directly regulated by ceramide: Reconstitution of SPT regulation in isolated membranes
- PMID: 30700557
- PMCID: PMC6442065
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.007291
The ORMDL/Orm-serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT) complex is directly regulated by ceramide: Reconstitution of SPT regulation in isolated membranes
Abstract
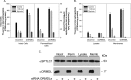
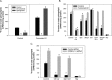
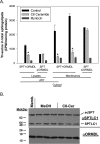
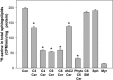
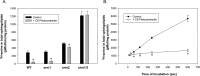
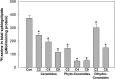
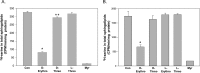
Sphingolipids compose a lipid family critical for membrane structure as well as intra- and intercellular signaling. De novo sphingolipid biosynthesis is initiated by the enzyme serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT), which resides in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane. In both yeast and mammalian species, SPT activity is homeostatically regulated through small ER membrane proteins, the Orms in yeast and the ORMDLs in mammalian cells. These proteins form stable complexes with SPT. In yeast, the homeostatic regulation of SPT relies, at least in part, on phosphorylation of the Orms. However, this does not appear to be the case for the mammalian ORMDLs. Here, we accomplished a cell-free reconstitution of the sphingolipid regulation of the ORMDL-SPT complex to probe the underlying regulatory mechanism. Sphingolipid and ORMDL-dependent regulation of SPT was demonstrated in isolated membranes, essentially free of cytosol. This suggests that this regulation does not require soluble cytosolic proteins or small molecules such as ATP. We found that this system is particularly responsive to the pro-apoptotic sphingolipid ceramide and that this response is strictly stereospecific, indicating that ceramide regulates the ORMDL-SPT complex via a specific binding interaction. Yeast membranes harboring the Orm-SPT system also directly responded to sphingolipid, suggesting that yeast cells have, in addition to Orm phosphorylation, an additional Orm-dependent SPT regulatory mechanism. Our results indicate that ORMDL/Orm-mediated regulation of SPT involves a direct interaction of sphingolipid with the membrane-bound components of the SPT-regulatory apparatus.
Keywords: cell signaling; endoplasmic reticulum (ER); homeostasis; lipid metabolism; lipid signaling; phytoceramide; sphingolipid; sphingomyelin; sphingosine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

