Expression of the Pseudorabies Virus gB Glycoprotein Triggers NK Cell Cytotoxicity and Increases Binding of the Activating NK Cell Receptor PILRβ
- PMID: 30700600
- PMCID: PMC6430535
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02107-18
Expression of the Pseudorabies Virus gB Glycoprotein Triggers NK Cell Cytotoxicity and Increases Binding of the Activating NK Cell Receptor PILRβ
Abstract
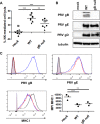
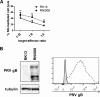
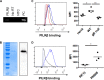
Natural killer (NK) cells are components of the innate immunity and are key players in the defense against virus-infected and malignant cells. NK cells are particularly important in the innate defense against herpesviruses, including alphaherpesviruses. Aggravated and life-threatening alphaherpesvirus-induced disease has been reported in patients with NK cell deficiencies. NK cells are regulated by a diversity of activating and inhibitory cell surface receptors that recognize specific ligands on the plasma membrane of virus-infected or malignant target cells. Although alphaherpesviruses have developed several evasion strategies against NK cell-mediated attack, alphaherpesvirus-infected cells are still readily recognized and killed by NK cells. However, the (viral) factors that trigger NK cell activation against alphaherpesvirus-infected cells are largely unknown. In this study, we show that expression of the gB glycoprotein of the alphaherpesvirus pseudorabies virus (PRV) triggers NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity, both in PRV-infected and in gB-transfected cells. In addition, we report that, like their human and murine counterpart, porcine NK cells express the activating receptor paired immunoglobulin-like type 2 receptor beta (PILRβ), and we show that gB expression triggers increased binding of recombinant porcine PILRβ to the surfaces of PRV-infected cells and gB-transfected cells.IMPORTANCE Natural killer (NK) cells display a prominent cytolytic activity against virus-infected cells and are indispensable in the innate antiviral response, particularly against herpesviruses. Despite their importance in the control of alphaherpesvirus infections, relatively little is known about the mechanisms that trigger NK cell cytotoxicity against alphaherpesvirus-infected cells. Here, using the porcine alphaherpesvirus pseudorabies virus (PRV), we found that the conserved alphaherpesvirus glycoprotein gB triggers NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity, both in virus-infected and in gB-transfected cells. In addition, we report that gB expression results in increased cell surface binding of porcine paired immunoglobulin-like type 2 receptor beta (PILRβ), an activating NK cell receptor. The interaction between PILRβ and viral gB may have consequences that stretch beyond the interaction with NK cells, including virus entry into host cells. The identification of gB as an NK cell-activating viral protein may be of importance in the construction of future vaccines and therapeutics requiring optimized interactions of alphaherpesviruses with NK cells.
Keywords: NK cells; PILRβ; glycoprotein gB; herpes; natural killer cells; pseudorabies virus.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pseudorabies Virus US3 Protein Kinase Protects Infected Cells from NK Cell-Mediated Lysis via Increased Binding of the Inhibitory NK Cell Receptor CD300a.J Virol. 2015 Nov 18;90(3):1522-33. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02902-15. Print 2016 Feb 1. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26581992 Free PMC article.
-
Porcine NK Cells Stimulate Proliferation of Pseudorabies Virus-Experienced CD8+ and CD4+CD8+ T Cells.Front Immunol. 2019 Jan 17;9:3188. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03188. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30705681 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of CD112 by the alphaherpesvirus gD protein suppresses DNAM-1-dependent NK cell-mediated lysis of infected cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Nov 11;111(45):16118-23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1409485111. Epub 2014 Oct 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25352670 Free PMC article.
-
Herpesvirus Evasion of Natural Killer Cells.J Virol. 2018 May 14;92(11):e02105-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02105-17. Print 2018 Jun 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29540598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral Evasion of Natural Killer Cell Activation.Viruses. 2016 Apr 12;8(4):95. doi: 10.3390/v8040095. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27077876 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pseudorabies Virus Glycoproteins E and B Application in Vaccine and Diagnosis Kit Development.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Sep 20;12(9):1078. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12091078. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39340108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host cellular factors involved in pseudorabies virus attachment and entry: a mini review.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Nov 27;10:1314624. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1314624. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 38089700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a Porcine Liver EomeshighT-betlow NK Cell Subset That Resembles Human Liver Resident NK Cells.Front Immunol. 2019 Oct 31;10:2561. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02561. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31736976 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarker identification for Alzheimer's disease through integration of comprehensive Mendelian randomization and proteomics data.J Transl Med. 2025 Mar 6;23(1):278. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06317-5. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40050982 Free PMC article.
-
Alphaherpesvirus gB Homologs Are Targeted to Extracellular Vesicles, but They Differentially Affect MHC Class II Molecules.Viruses. 2020 Apr 10;12(4):429. doi: 10.3390/v12040429. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32290097 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almerigogna F, Fassio F, Giudizi MG, Biagiotti R, Manuelli C, Chiappini E, Galli L, Romagnani S, De Martino M. 2011. Natural killer cell deficiencies in a consecutive series of children with herpetic encephalitis. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 24:231–238. doi:10.1177/039463201102400128. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

