A quantitative approach for measuring the reservoir of latent HIV-1 proviruses
- PMID: 30700913
- PMCID: PMC6447073
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-0898-8
A quantitative approach for measuring the reservoir of latent HIV-1 proviruses
Abstract
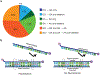
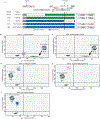
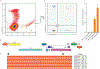
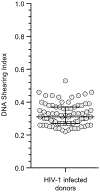
A stable latent reservoir for HIV-1 in resting CD4+ T cells is the principal barrier to a cure1-3. Curative strategies that target the reservoir are being tested4,5 and require accurate, scalable reservoir assays. The reservoir was defined with quantitative viral outgrowth assays for cells that release infectious virus after one round of T cell activation1. However, these quantitative outgrowth assays and newer assays for cells that produce viral RNA after activation6 may underestimate the reservoir size because one round of activation does not induce all proviruses7. Many studies rely on simple assays based on polymerase chain reaction to detect proviral DNA regardless of transcriptional status, but the clinical relevance of these assays is unclear, as the vast majority of proviruses are defective7-9. Here we describe a more accurate method of measuring the HIV-1 reservoir that separately quantifies intact and defective proviruses. We show that the dynamics of cells that carry intact and defective proviruses are different in vitro and in vivo. These findings have implications for targeting the intact proviruses that are a barrier to curing HIV infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
Additonal References for Methods Section
-
- Rose PP & Korber BT Detecting hypermutations in viral sequences with an emphasis on G --> A hypermutation. Bioinformatics 16, 400–401 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Laird GM, Rosenbloom DI, Lai J, Siliciano RF & Siliciano JD Measuring the Frequency of Latent HIV-1 in Resting CD4(+) T Cells Using a Limiting Dilution Coculture Assay. Methods Mol. Biol 1354, 239–253 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R43 AI124996/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007445/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- U01 HL146201/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI043222/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R61 DA047022/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI12661/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI131374/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI126620/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035042/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI131306/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI126603/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R44 AI124996/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

