The Burden of HIV/AIDS in Ethiopia from 1990 to 2016: Evidence from the Global Burden of Diseases 2016 Study
- PMID: 30700953
- PMCID: PMC6341438
- DOI: 10.4314/ejhs.v29i1.7
The Burden of HIV/AIDS in Ethiopia from 1990 to 2016: Evidence from the Global Burden of Diseases 2016 Study
Abstract
Background: The burden of HIV/AIDS in Ethiopia has not been comprehensively assessed over the last two decades. In this study, we used the 2016 Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries and Risk factors (GBD) data to analyze the incidence, prevalence, mortality and Disability-adjusted Life Years Lost (DALY) rates of Human Immunodeficiency Virus / Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (HIV/AIDS) in Ethiopia over the last 26 years.
Methods: The GBD 2016 used a wide range of data source for Ethiopia such as verbal autopsy (VA), surveys, reports of the Federal Ministry of Health and the United Nations (UN) and published scientific articles. The modified United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) Spectrum model was used to estimate the incidence and mortality rates for HIV/AIDS.
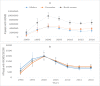
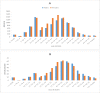
Results: In 2016, an estimated 36,990 new HIV infections (95% uncertainty interval [UI]: 8775-80262), 670,906 prevalent HIV cases (95% UI: 568,268-798,970) and 19,999 HIV deaths (95% UI: 16426-24412) occurred in Ethiopia. The HIV/AIDS incidence rate peaked in 1995 and declined by 6.3% annually for both sexes with a total reduction of 77% between 1990 and 2016. The annualized HIV/AIDS mortality rate reduction during 1990 to 2016 for both sexes was 0.4%.
Conclusions: Ethiopia has achieved the 50% reduction of the incidence rate of HIV/AIDS based on the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) target. However, the decline in HIV/AIDS mortality rate has been comparatively slow. The country should strengthen the HIV/AIDS detection and treatment programs at community level to achieve its targets during the Sustainable Development Program (SDGs)-era.
Keywords: Burden; Ethiopia; GBD; HIV/AIDS.
Figures

References
-
- WHO, author. From MDG To SDG. World Health Organization(WHO); 2015. [November 28, 2017]. ( Http://Apps.Who.Int/Iris/Bitstream/10665/200009/1/9789241565110_Eng.Pdf?...)
-
- UN, author. The Millennium Development Goals Report. United Nations; 2015.
-
- WHO, author. HIV/AIDS. Fact Sheet. World Health Organization(WHO); [August 24, 2018]. ( Http://Www.Who.Int/Mediacentre/Factsheets/Fs360/En/2016)
-
- FMOH, author. HIV Epidemic Estimates By Regional States And Ethiopia. FMOH(Federal Ministry Of Health), HIV/AIDS Prevention And Control Office; 2015.
-
- UNAIDS, author. Ending AIDS: Progress Towards The 90-90-90 Targets. UNAIDS; 2016.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
