Biocompatible Peritoneal Dialysis: The Target Is Still Way Off
- PMID: 30700974
- PMCID: PMC6343681
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01853
Biocompatible Peritoneal Dialysis: The Target Is Still Way Off
Abstract
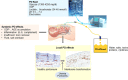
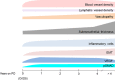
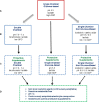
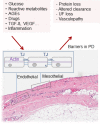
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a cost-effective, home-based therapy for patients with end-stage renal disease achieving similar outcome as compared to hemodialysis. Still, a minority of patients only receive PD. To a significant extend, this discrepancy is explained by major limitations regarding PD efficiency and sustainability. Due to highly unphysiological composition of PD fluids, the peritoneal membrane undergoes rapid morphological and long-term functional alterations, which limit the treatment and contribute to adverse patient outcome. This review is focused on the peritoneal membrane ultrastructure and its transformation in patients with kidney disease and chronic PD, underlying molecular mechanisms, and potential systemic sequelae. Current knowledge on the impact of conventional and second-generation PD fluids is described; novel strategies and innovative PD fluid types are discussed.
Keywords: biocompatibility; glucose; glucose degradation products; junctions; peritoneal dialysis; peritoneum; transformation; transport.
Figures
References
-
- Aroeira L. S., Aguilera A., Sánchez-Tomero J. A., Bajo M. A., del Peso G., Jiménez-Heffernan J. A., et al. . (2007). Epithelial to mesenchymal transition and peritoneal membrane failure in peritoneal dialysis patients: pathologic significance and potential therapeutic interventions. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 18, 2004–2013. 10.1681/ASN.2006111292, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aufricht C., Beelen R., Eberl M., Fischbach M., Fraser D., Jorres A., et al. . (2017). Biomarker research to improve clinical outcomes of peritoneal dialysis: consensus of the European Training and Research in Peritoneal Dialysis (EuTRiPD) network. Kidney Int. 92, 824–835. 10.1016/j.kint.2017.02.037, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bajo M. A., Perez-Lozano M. L., Albar-Vizcaino P., del Peso G., Castro M. J., Gonzalez-Mateo G., et al. . (2011). Low-GDP peritoneal dialysis fluid (‘balance’) has less impact in vitro and ex vivo on epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of mesothelial cells than a standard fluid. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 26, 282–291. 10.1093/ndt/gfq357, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

