Ulcerated Lesions of the Oral Mucosa: Clinical and Histologic Review
- PMID: 30701449
- PMCID: PMC6405793
- DOI: 10.1007/s12105-018-0981-8
Ulcerated Lesions of the Oral Mucosa: Clinical and Histologic Review
Abstract
Ulcerated lesions of the oral cavity have many underlying etiologic factors, most commonly infection, immune related, traumatic, or neoplastic. A detailed patient history is critical in assessing ulcerative oral lesions and should include a complete medical and medication history; whether an inciting or triggering trauma, condition, or medication can be identified; the length of time the lesion has been present; the frequency of episodes in recurrent cases; the presence or absence of pain; and the growth of the lesion over time. For multiple or recurrent lesions the presence or history of ulcers on the skin, genital areas, or eyes should be evaluated along with any accompanying systemic symptoms such as fever, arthritis, or other signs of underlying systemic disease. Biopsy may be indicated in many ulcerative lesions of the oral cavity although some are more suitable for clinical diagnosis. Neoplastic ulcerated lesions are notorious in the oral cavity for their ability to mimic benign ulcerative lesions, highlighting the essential nature of biopsy to establish a diagnosis in cases that are not clinically identifiable or do not respond as expected to treatment. Adjunctive tests may be required for final diagnosis of some ulcerated lesions especially autoimmune lesions. Laboratory tests or evaluation to rule out systemic disease may be also required for recurrent or severe ulcerations especially when accompanied by other symptoms. This discussion will describe the clinical and histopathologic characteristics of a variety of ulcerated lesions found in the oral cavity.
Keywords: Aphthous stomatitis; Herpetic gingivostomatitis; Oral erythema multiforme; Oral lichen planus; Oral lymphoma; Oral medication related ulcer; Oral squamous cell carcinoma; Oral ulcer; Oral vesiculobullous lesions; Traumatic oral ulcer.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Ethics Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animal performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Not applicable for this article.
Figures

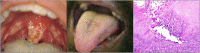
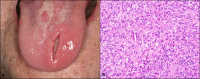
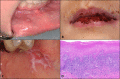
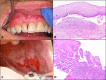
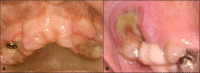


References
-
- Leão JC, Gueiros LA, Porter SR. Oral manifestations of syphilis. Clinics. 2006;61:161–166. - PubMed
-
- Alam F, Argiriadou AS, Hodgson TA, et al. Primary syphilis remains a cause of oral ulceration. Br Dent J. 2000;189:352–354. - PubMed
-
- Little JW. Syphilis: an update. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005;100:3–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

