Contrasting performance between physically active and sedentary older people playing exergames
- PMID: 30702574
- PMCID: PMC6380728
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014213
Contrasting performance between physically active and sedentary older people playing exergames
Abstract
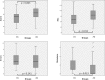
The increase in life expectancy associated with the increase in chronological age and less active people helps in the appearance of chronic and degenerative diseases. The encouragement of physical exercises contributes to older people abandoning sedentarism and preventing such diseases. Exergame is a promising alternative, for making exercise a pleasurable activity.In this study, we compared the performance of physically active older people with sedentary older people in exergames.Participants were 83 older adults over 65 years of age, of both sexes, divided into 2 physically active older people (AG) and sedentary older people (CG) groups. The participants performed a task through an exergame called "MoviLetrando" that uses the score, number of hits, number of omissions, and an average time of hits as an evaluation. A characterization questionnaire was applied, with information about sex, age, marital status, economic class, self-rated health, time of use of electronic games, a questionnaire on the practice of physical activity, and the Brunel Mood Scale.There was a higher exergame score in AG than in CG (P = .003), in the number of correct answers (P = .012). The number of omissions was lower in AG than in CG (P = .023). The mean time of correct answers was lower in AG than in CG (P = .013). The regression analysis revealed a significant finding F (3, 82) = 11.06, P < .001 and showed a prediction ability of 26.9% (r = .269). Three variables remained significantly associated with the score: physical activity was marginally significant (β = .19, P = .06), age (β = -.403, P < .001), depression (β = -.212, P = .028).Physically active older people perform better when compared with the sedentary older people. Age, depression, and physical activity influence the performance in exergame.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
EXERGAMES IN ADOLESCENTS: ASSOCIATED FACTORS AND POSSIBLE REDUCTION IN SEDENTARY TIME.Rev Paul Pediatr. 2019 Oct 10;37(4):442-449. doi: 10.1590/1984-0462/;2019;37;4;00019. eCollection 2019. Rev Paul Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31621789 Free PMC article.
-
Exergaming as a Physical Exercise Strategy Reduces Frailty in People With Dementia: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2019 Dec;20(12):1502-1508.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2019.06.026. Epub 2019 Aug 10. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2019. PMID: 31409559 Clinical Trial.
-
Erratum.Mult Scler. 2016 Oct;22(12):NP9-NP11. doi: 10.1177/1352458515585718. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Mult Scler. 2016. PMID: 26041800
-
Exergames to Limit Weight Gain and to Fight Sedentarism in Children and Adolescents with Obesity.Children (Basel). 2023 May 24;10(6):928. doi: 10.3390/children10060928. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37371160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of exergames on muscle strength: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2021 Aug;31(8):1592-1611. doi: 10.1111/sms.13964. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2021. PMID: 33797115
Cited by
-
Effect of Combined Therapy of Virtual Reality and Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation in Children and Adolescents With Cerebral Palsy: A Study Protocol for a Triple-Blinded Randomized Controlled Crossover Trial.Front Neurol. 2020 Sep 2;11:953. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00953. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32982950 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Specific Mood Profile Clusters among Elite and Youth Athletes at a Brazilian Sports Club.Sports (Basel). 2024 Jul 18;12(7):195. doi: 10.3390/sports12070195. Sports (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39058086 Free PMC article.
-
Serious Game Platform as a Possibility for Home-Based Telerehabilitation for Individuals With Cerebral Palsy During COVID-19 Quarantine - A Cross-Sectional Pilot Study.Front Psychol. 2021 Feb 2;12:622678. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.622678. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 33633648 Free PMC article.
-
Comment on: Problematic online gaming and the COVID-19 pandemic - The role of exergames.J Behav Addict. 2021 Mar 4;10(1):1-3. doi: 10.1556/2006.2021.00014. J Behav Addict. 2021. PMID: 33666566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global Health and Aging. 2011. Available at: http://www.who.int/ageing/publications/global_health.pdf Accessed May 2017.
-
- Farias EH, de Oliveira HC, Hounsell MDS, Rossito GM. MOLDE: a Methodology for Serious Games Measure-Oriented Level Design. XIII SBGames; Porto Alegre, RS 2014.
-
- Tribess S, Virtuoso JR, Jair S. Prescrição de exercício físico para idosos. Rev Saúde Com 2005;2:163–72.
-
- Gonçalves AK, Groenwald RMF. Qualidade de Vida e Estilo de Vida Ativo no Envelhecimento. Porto Alegre: Novo Tempo; 2005.
-
- Netto M, Ponte JR. Envelhecimento: Desafio na Transição do Século. São Paulo: Editora Atheneu; 2005.

