Attenuation of Allergen-, IL-13-, and TGF-α-induced Lung Fibrosis after the Treatment of rIL-15 in Mice
- PMID: 30702923
- PMCID: PMC6604217
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2018-0254OC
Attenuation of Allergen-, IL-13-, and TGF-α-induced Lung Fibrosis after the Treatment of rIL-15 in Mice
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Attenuation of Allergen-, IL-13-, and TGF-α-induced Lung Fibrosis after the Treatment of rIL-15 in Mice.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021 Aug;65(2):229-230. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.v65erratum2. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34328408 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
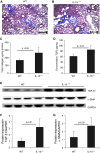
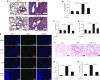
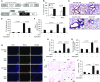
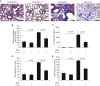
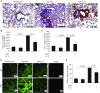
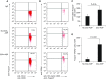
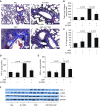
Endogenous IL-15 deficiency promotes lung fibrosis; therefore, we examined the effect of induced IL-15 in restricting the progression of lung fibrosis. Our objective in this work was to establish a novel therapeutic molecule for pulmonary fibrosis. Western blot, qPCR, and ELISA were performed on the lung tissues of IL-15-deficient mice, and recombinant IL-15 (rIL-15)-treated CC10-IL-13 and CC10-TGF-α mice, and allergen-challenged CC10-IL-15 mice were examined to establish the antifibrotic effect of IL-15 in lung fibrosis. We show that endogenous IL-15 deficiency induces baseline profibrotic cytokine and collagen accumulation in the lung, and pharmacological delivery of rIL-15 downregulates Aspergillus antigen-induced lung collagen, the profibrotic cytokines IL-13 and TGF-β1, and α-SMA+ and FSP1+ cells in mice. To confirm that overexpression of IL-15 diminishes pulmonary fibrosis, we generated CC10-rtTA-tetO7-IL-15 transgenic mice and challenged them with Aspergillus antigen. Aspergillus antigen-challenged, doxycycline (DOX)-treated CC10-IL-15 transgenic mice exhibited decreased collagen accumulation, profibrotic cytokine (IL-13 and TGF-β1) expression, and α-SMA+ and FSP1+ cells compared with IL-15-overexpressing mice not treated with DOX. Additionally, to establish that the antifibrotic effect of IL-15 is not limited to allergen-induced fibrosis, we showed that rIL-15 or IL-15 agonist treatment restricted pulmonary fibrosis even in CC10-IL-13 and CC10-TGF-α mice. Mechanistically, we show that T-helper cell type 17 suppressor IL-15-responsive RORγ+ T regulatory cells are induced in DOX-treated, allergen-challenged IL-15-overexpressing mice, which may be a novel pathway for restricting progression of pulmonary fibrosis. Taken together, our data establishes antifibrotic activity of IL-15 that might be a novel therapeutic molecule to combat the development of pulmonary fibrosis.
Keywords: IL-13; TGF-β; allergen; fibrosis; lung.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulatory effects of IL-15 on allergen-induced airway obstruction.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018 Mar;141(3):906-917.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.05.025. Epub 2017 Jun 9. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 28606589 Free PMC article.
-
IL-15 regulates fibrosis and inflammation in a mouse model of chronic pancreatitis.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018 Dec 1;315(6):G954-G965. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00139.2018. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30212254 Free PMC article.
-
Conditional expression of transforming growth factor-alpha in adult mouse lung causes pulmonary fibrosis.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2004 Apr;286(4):L741-9. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00208.2003. Epub 2003 Dec 5. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14660483
-
Fucoxanthin inhibits profibrotic protein expression in vitro and attenuates bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in vivo.Eur J Pharmacol. 2017 Sep 15;811:199-207. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.06.022. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28642129
-
Pulmonary fibrosis: Therapeutic and mechanistic insights into the role of phytochemicals.Biofactors. 2021 May;47(3):250-269. doi: 10.1002/biof.1713. Epub 2021 Feb 6. Biofactors. 2021. PMID: 33548106 Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin (IL)-15 significance in aging associated asthma pathogenesis.Int J Cell Biol Physiol. 2020;3:https://zenodo.org/record/4393736. Epub 2020 Dec 25. Int J Cell Biol Physiol. 2020. PMID: 34027517 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Sex Hormones and Lung Inflammation.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1304:259-321. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-68748-9_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34019274
-
Profibrogenic role of IL-15 through IL-15 receptor alpha-mediated trans-presentation in the carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis model.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 11;15:1404891. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1404891. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38919611 Free PMC article.
-
Erratum: Attenuation of Allergen-, IL-13-, and TGF-α-induced Lung Fibrosis after the Treatment of rIL-15 in Mice.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021 Aug;65(2):229-230. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.v65erratum2. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34328408 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
IL-15 immunotherapy is a viable strategy for COVID-19.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020 Aug;54:24-31. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.06.008. Epub 2020 Jun 6. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020. PMID: 32536564 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hogan SP, Matthaei KI, Young JM, Koskinen A, Young IG, Foster PS. A novel T cell-regulated mechanism modulating allergen-induced airways hyperreactivity in BALB/c mice independently of IL-4 and IL-5. J Immunol. 1998;161:1501–1509. - PubMed
-
- Robinson DS, Hamid Q, Ying S, Tsicopoulos A, Barkans J, Bentley AM, et al. Predominant TH2-like bronchoalveolar T-lymphocyte population in atopic asthma. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:298–304. - PubMed
-
- Quesnel C, Nardelli L, Piednoir P, Leçon V, Marchal-Somme J, Lasocki S, et al. Alveolar fibroblasts in acute lung injury: biological behaviour and clinical relevance. Eur Respir J. 2010;35:1312–1321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

