Anticytokine Agents: Targeting Interleukin Signaling Pathways for the Treatment of Atherothrombosis
- PMID: 30702995
- PMCID: PMC6386195
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.313129
Anticytokine Agents: Targeting Interleukin Signaling Pathways for the Treatment of Atherothrombosis
Abstract
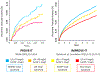
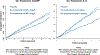
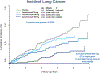
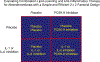
The recognition that atherosclerosis is a complex chronic inflammatory disorder mediated through both adaptive and innate immunity has led to the hypothesis that anticytokine therapies targeting specific IL (interleukin) signaling pathways could serve as powerful adjuncts to lipid lowering in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease. Cytokines involved in human atherosclerosis can be broadly classified as proinflammatory and proatherogenic (such as IL-1, IL-6, and TNF [tumor necrosis factor]) or as anti-inflammatory and antiatherogenic (such as IL-10 and IL-1rA). The recent CANTOS (Canakinumab Anti-Inflammatory Thrombosis Outcomes Study) has shown that specific targeting of IL-1β can significantly reduce cardiovascular event rates without lipid or blood pressure lowering. In CANTOS, the magnitude of benefit of this cytokine-targeted approach to atherosclerosis treatment was associated to the magnitude of reduction of the central signaling cytokine IL-6 and the downstream clinical biomarker high-sensitivity CRP (C-reactive protein). By contrast, in the recent CIRT (Cardiovascular Inflammation Reduction Trial), low-dose methotrexate neither reduced IL-1β, IL-6, or high-sensitivity CRP nor lowered cardiovascular event rates. Taken together, these 2 contemporary trials provide proof of principle that focused cytokine inhibition, not broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory therapy, is likely to be crucial for atheroprotection. This review provides an overview of cytokines in atherosclerosis, the potential benefits and risks associated with targeted anticytokine therapies, and a look to the future of clinical practices addressing residual inflammatory risk.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; cytokines; humans; inflammasomes; interleukins.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
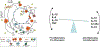
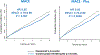

Similar articles
-
Interleukin-6 Signaling and Anti-Interleukin-6 Therapeutics in Cardiovascular Disease.Circ Res. 2021 May 28;128(11):1728-1746. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.319077. Epub 2021 May 17. Circ Res. 2021. PMID: 33998272 Review.
-
Closing the loop on inflammation and atherothrombosis: why perform the CIRT and CANTOS trials?Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 2013;124:174-90. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 2013. PMID: 23874021 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of the interleukin-6 signalling pathway and incidence rates of atherosclerotic events and all-cause mortality: analyses from the Canakinumab Anti-Inflammatory Thrombosis Outcomes Study (CANTOS).Eur Heart J. 2018 Oct 7;39(38):3499-3507. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy310. Eur Heart J. 2018. PMID: 30165610 Clinical Trial.
-
Anticytokine Immune Therapy and Atherothrombotic Cardiovascular Risk.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019 Aug;39(8):1510-1519. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.311998. Epub 2019 Jul 11. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019. PMID: 31294625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-1β inhibition and the prevention of recurrent cardiovascular events: rationale and design of the Canakinumab Anti-inflammatory Thrombosis Outcomes Study (CANTOS).Am Heart J. 2011 Oct;162(4):597-605. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2011.06.012. Epub 2011 Sep 14. Am Heart J. 2011. PMID: 21982649 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Induced Inflammatory and Oxidative Markers in Cerebral Microvasculature by Mentally Depressive Stress.Mediators Inflamm. 2023 Feb 18;2023:4206316. doi: 10.1155/2023/4206316. eCollection 2023. Mediators Inflamm. 2023. PMID: 36852396 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating microRNAs in Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Carotid Stenosis.Front Neurol. 2021 Nov 24;12:755827. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.755827. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34899574 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Differences in Proatherogenic Cytokine Levels.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 29;21(11):3861. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113861. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32485823 Free PMC article.
-
Functional role of skeletal muscle-derived interleukin-6 and its effects on lipid metabolism.Front Physiol. 2023 Jul 24;14:1110926. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1110926. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37555019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory Therapies for Coronary Heart Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Aug 25;8:726341. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.726341. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34513960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hansson GK. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 2005;352:1685–95. - PubMed
-
- Libby P, Ridker PM, Hansson GK. Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis. Nature 2011;473:317–25 - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM. How common is residual inflammatory risk? Circ Res 2017;120:617–619. - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM, Everett B, Thuren T, Macfadyen JG, Chang WH, Ballantyne C, Fonseca F, Nicolau J, Koenig W, Anker SD, Kastelein JJP, Cornel JH, Pais P, Pella D, Genest J, Cifkova A, Lorenzatti A, Forster T, Kobalava Z, Vida-Smith L, Flather M, Shimokowa H, Ogawa H, Dellborg M, Rossi PRF, Troquay RPT, Libby P, Glynn RJ for the CANTOS Trial Group. Antiinflammatory therapy with canakinumab for atherosclerotic disease. N Engl J Med 2017;377:1119–1131. - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM, Everett BM, Pradhan A, MacFadyen JG, Solomon DH, Zaharris E, Mam V, Hasan A, Rosenberg Y, Iturriaga E, Gupta M, Tsigoulis M, Verma S, Clearfield M, Libby P, Goldhaber SZ, Seagle R, Ofori C, Saklayen M, Butman S, Singh N, Le May M, Bertrand O, Johnston J, Paynter NP, Glynn RJ for the Cardiovascular Inflammation Reduction Trial (CIRT) Investigators. Low dose methotrexate for the prevention of atherosclerotic events. N Engl J Med 2018. (on line November 10)DOI 10.1056/NEJMoa1809798. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

