A Clinical Phase II Study to Assess Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Waterfree Cyclosporine Formulation for Treatment of Dry Eye Disease
- PMID: 30703441
- PMCID: PMC8554539
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2019.01.024
A Clinical Phase II Study to Assess Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Waterfree Cyclosporine Formulation for Treatment of Dry Eye Disease
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of waterfree cyclosporine formulation (CyclASol) at 2 concentrations (0.1% and 0.05% of cyclosporine [CsA]) to vehicle when applied twice daily for 16 weeks in patients with dry eye disease (DED). An open-label Restasis (Allergan, Irvine, CA) arm was included to allow a direct comparison with an approved therapy.
Design: An exploratory phase II, multicenter, randomized, vehicle-controlled clinical trial, double-masked between CyclASol and vehicle with an open-label comparator.
Participants: Two hundred and seven eligible patients with a history of dry eye disease were randomized 1:1:1:1 to 1 of 4 treatment arms (CyclASol 0.05%, n = 51; CyclASol 0.1%, n = 51; vehicle, n = 52, and Restasis, n = 53).
Methods: After a 2-week run-in period with twice-daily dosing of Systane Balance (Alcon, Fort Worth, TX), patients were randomized to the respective treatment arm and dosed twice daily for 16 weeks.
Main outcome measures: The study was set up to explore efficacy on a number of sign and symptom end points including total and subregion corneal fluorescein staining, conjunctival staining, visual analog scale (VAS) for dry eye symptoms VAS severity, and Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI) questionnaire.
Results: CyclASol showed a consistent reduction in corneal and conjunctival staining compared with both vehicle and Restasis over the 16-week treatment period, with an early onset of effect (at day 14). A mixed-effects model-based approach demonstrated that the CyclASol drug effect was statistically significant over vehicle (total corneal staining P < 0.1, central corneal staining P < 0.001, conjunctival staining P < 0.01). This model-based analysis suggests a significant CyclASol effect for OSDI as symptom parameter (P < 0.01). The numbers of ocular adverse events were low in all treatment groups.
Conclusions: CyclASol showed efficacy, safety, and tolerability at 2 concentrations in moderate-to-severe DED. In a direct head-to-head against open-label Restasis, CyclASol was found to have an earlier onset of action, as early as after 2 weeks of treatment, in relieving the signs of DED, as measured by corneal and conjunctival staining. The central region of the cornea, an important area for visual function in dry eye sufferers, was shown to have the most benefit from treatment. Excellent safety, tolerability, and comfort profile supports this new CsA formulation as having a positive benefit-to-risk ratio.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02617667.
Copyright © 2018 American Academy of Ophthalmology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


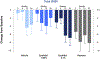
References
-
- Schiffman RM, Walt JG, Jacobsen G, et al. Utility assessment among patients with dry eye disease. Ophthalmology. 2003;110:1412–1419. - PubMed
-
- Lallemand F, Felt-Baeyens O, Besseghir K, et al. Cyclosporine A delivery to the eye: a pharmaceutical challenge. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2003;56:307–318. - PubMed
-
- Sall K, Stevenson OD, Mundorf TK, Reis BL. CsA Phase 3 study group, two randomized studies of the efficacy and safety of cyclosporine ophthalmic emulsion in moderate to severe dry eye disease. Ophthalmology. 2000;107:631–639. - PubMed
-
- Dutescu RM, Panfil C, Merkel UM, et al. Semifluorinated alkanes as a liquid drug carrier system for topical ocular drug delivery. E J Pham Biopharm. 2014;88:123–128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

