Polypeptide GalNAc-Ts: from redundancy to specificity
- PMID: 30703750
- PMCID: PMC6656595
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2018.12.007
Polypeptide GalNAc-Ts: from redundancy to specificity
Abstract
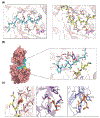
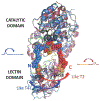
Mucin-type O-glycosylation is a post-translational modification (PTM) that is predicted to occur in more than the 80% of the proteins that pass through the Golgi apparatus. This PTM is initiated by a family of polypeptide GalNAc-transferases (GalNAc-Ts) that modify Ser and Thr residues of proteins through the addition of a GalNAc moiety. These enzymes are type II membrane proteins that consist of a Golgi luminal catalytic domain connected by a flexible linker to a ricin type lectin domain. Together, both domains account for the different glycosylation preferences observed among isoenzymes. Although it is well accepted that most of the family members share some degree of redundancy toward their protein and glycoprotein substrates, it has been recently found that several GalNAc-Ts also possess activity toward specific targets. Despite the high similarity between isoenzymes, structural differences have recently been reported that are key to understanding the molecular basis of both their redundancy and specificity. The present review focuses on the molecular aspects of the protein substrate recognition and the different glycosylation preferences of these enzymes, which in turn will serve as a roadmap to the rational design of specific modulators of mucin-type O-glycosylation.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Bennett EP, Mandel U, Clausen H, Gerken TA, Fritz TA, Tabak LA: Control of mucin-type O-glycosylation: A classification of the polypeptide GalNAc-transferase gene family. Glycobiology (2011) 22(6):736–756. - PMC - PubMed
-
This work provides an overview of the GalNAc-Ts family members, as well as a classification of its isoenzymes according to their glycosylation preferences.
-
- Hollingsworth MA, Swanson BJ: Mucins in cancer: Protection and control of the cell surface. Nature Reviews Cancer (2004) 4(1):45–60. - PubMed
-
- Revoredo L, Wang S, Bennett EP, Clausen H, Moremen KW, Jarvis DL, Ten Hagen KG, Tabak LA, Gerken TA: Mucin-type O-glycosylation is controlled by short-and long-range glycopeptide substrate recognition that varies among members of the polypeptide GalNAc transferase family. Glycobiology (2015) 26(4):360–376. - PMC - PubMed
-
This work digs into the glycosylation preferences of the different GalNAc-Ts isoenzymes and demonstrate that catalytic and lectin domains have unique functions and work in concert to direct glycosylation. The authors propose a more exhaustive re-classification of the family members.
-
- Pratt MR, Hang HC, Ten Hagen KG, Rarick J, Gerken TA, Tabak LA, Bertozzi CR: Deconvoluting the functions of polypeptide N-α-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase family members by glycopeptide substrate profiling. Chemistry & biology (2004) 11(7):1009–1016. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

