CYT997(Lexibulin) induces apoptosis and autophagy through the activation of mutually reinforced ER stress and ROS in osteosarcoma
- PMID: 30704503
- PMCID: PMC6357486
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-019-1047-9
CYT997(Lexibulin) induces apoptosis and autophagy through the activation of mutually reinforced ER stress and ROS in osteosarcoma
Abstract
Background: Osteosarcoma (OS) is a common malignant cancer in children and adolescents and has a cure rate that has not improved in the last two decades. CYT997 (lexibulin) is a novel potent microtubule-targeting agent with various anticancer activities, such as proliferation inhibition, vascular disruption, and cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction, in multiple cancers. However, the direct cytotoxic mechanisms of CYT997 have not yet been fully characterized.
Methods: We evaluated apoptosis and autophagy in human osteosarcomas after treatment with CYT997 and investigated the underlying mechanisms. To explore relationships, we used the reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenger N-acetyl cysteine (NAC), PERK inhibitor GSK2606414, ERO1 inhibitor EN460 and mitochondrial targeted protection peptide elamipretide. BALB/c-nu mice were inoculated with 143B tumor cells to investigate the in vivo effect of CYT997.
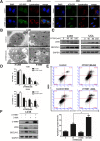
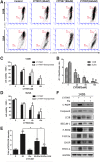
Results: We explored the efficacy and mechanism of CYT997 in osteosarcoma (OS) in vitro and in vivo and demonstrated that CYT997 potently suppresses cell viability and induces apoptosis and autophagy. CYT997 triggered production of ROS and exerted lethal effects via endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in OS cells. NAC attenuated these effects. The PERK inhibitor GSK2606414, which can block the ER stress pathway, reduced ROS production and enhanced cell viability. Moreover, activation of ERO1 in the ER stress pathway was responsible for inducing ROS production. ROS produced by the mitochondrial pathway also aggravate ER stress. Protection of mitochondria can reduce apoptosis and autophagy. Finally, CYT997 prominently reduced tumor growth in vivo.
Conclusions: This study suggests that CYT997 induces apoptosis and autophagy in OS cells by triggering mutually enhanced ER stress and ROS and may thus be a promising agent against OS.
Keywords: CYT997; ER stress; ERO1A; Osteosarcoma; ROS.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All procedures in this study were performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the Animal Care and Use Committee of Shanghai General Hospital and Shanghai Jiaotong University.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial ROS accumulation inhibiting JAK2/STAT3 pathway is a critical modulator of CYT997-induced autophagy and apoptosis in gastric cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Jun 23;39(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01621-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32576206 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy blockade sensitizes human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma towards CYT997 through enhancing excessively high reactive oxygen species-induced apoptosis.J Mol Med (Berl). 2018 Sep;96(9):929-938. doi: 10.1007/s00109-018-1670-5. Epub 2018 Jul 18. J Mol Med (Berl). 2018. PMID: 30022281
-
Erianin induces G2/M-phase arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy via the ROS/JNK signaling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells in vitro and in vivo.Cell Death Dis. 2016 Jun 2;7(6):e2247. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.138. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 27253411 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism and Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Osteosarcoma.Biomolecules. 2022 Dec 15;12(12):1882. doi: 10.3390/biom12121882. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36551309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell apoptosis, autophagy and necroptosis in osteosarcoma treatment.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 12;7(28):44763-44778. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8206. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27007056 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A possible connection between reactive oxygen species and the unfolded protein response in lens development: From insight to foresight.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 21;10:820949. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.820949. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36211466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps impair intestinal barrier functions in sepsis by regulating TLR9-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jun 11;12(6):606. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03896-1. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34117211 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the ERO1-PDI interaction in oxidative protein folding and disease.Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Jun;210:107525. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107525. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32201313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LINC01128 regulates the development of osteosarcoma by sponging miR-299-3p to mediate MMP2 expression and activating Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Dec;24(24):14293-14305. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16046. Epub 2020 Oct 27. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 33108067 Free PMC article.
-
hsa_circ_0085539 Promotes Osteosarcoma Progression by Regulating miR-526b-5p and SERP1.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020 Oct 4;19:163-177. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.09.009. eCollection 2020 Dec 16. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020. PMID: 33209976 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

