Sex and Pubertal Differences in the Type 1 Interferon Pathway Associate With Both X Chromosome Number and Serum Sex Hormone Concentration
- PMID: 30705679
- PMCID: PMC6345344
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03167
Sex and Pubertal Differences in the Type 1 Interferon Pathway Associate With Both X Chromosome Number and Serum Sex Hormone Concentration
Abstract
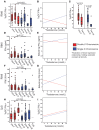
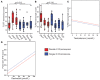
Type 1 interferons (IFN) are an antiviral cytokine family, important in juvenile onset systemic lupus erythematosus (jSLE) which is more common in females, around puberty. We report that plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDC) from healthy females produced more type 1 IFN after toll like receptor (TLR) 7 signaling than males, even before puberty, but that puberty itself associated with increased production of type 1 IFN. A unique human model allows us to show that this was related to X chromosome number, and serum testosterone concentration, in a manner which differed depending on the number of X chromosomes present. In addition, we have showed that pDC were more activated in females overall, and immune cell TLR7 gene expression was higher in females after puberty. Therefore, sex hormones and X chromosome number were associated individually and interactively with the type 1 IFN response, which contributes to our understanding of why females are more likely to develop an IFN mediated disease like jSLE after puberty.
Keywords: SLE; TLR7; X Chromosome; immunity; interferon; puberty; sex; sex hormone.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

