High efficiency Agrobacterium-mediated site-specific gene integration in maize utilizing the FLP-FRT recombination system
- PMID: 30706638
- PMCID: PMC6662307
- DOI: 10.1111/pbi.13089
High efficiency Agrobacterium-mediated site-specific gene integration in maize utilizing the FLP-FRT recombination system
Abstract
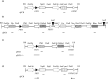
An efficient Agrobacterium-mediated site-specific integration (SSI) technology using the flipase/flipase recognition target (FLP/FRT) system in elite maize inbred lines is described. The system allows precise integration of a single copy of a donor DNA flanked by heterologous FRT sites into a predefined recombinant target line (RTL) containing the corresponding heterologous FRT sites. A promoter-trap system consisting of a pre-integrated promoter followed by an FRT site enables efficient selection of events. The efficiency of this system is dependent on several factors including Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain, expression of morphogenic genes Babyboom (Bbm) and Wuschel2 (Wus2) and choice of heterologous FRT pairs. Of the Agrobacterium strains tested, strain AGL1 resulted in higher transformation frequency than strain LBA4404 THY- (0.27% vs. 0.05%; per cent of infected embryos producing events). The addition of morphogenic genes increased transformation frequency (2.65% in AGL1; 0.65% in LBA4404 THY-). Following further optimization, including the choice of FRT pairs, a method was developed that achieved 19%-22.5% transformation frequency. Importantly, >50% of T0 transformants contain the desired full-length site-specific insertion. The frequencies reported here establish a new benchmark for generating targeted quality events compatible with commercial product development.
Keywords: Agrobacterium; RMCE; FLP/FRT; co-integrate vector; maize transformation; site-specific integration.
© 2019 The Authors. Plant Biotechnology Journal published by Society for Experimental Biology and The Association of Applied Biologists and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
AA, W.G‐K and EW are inventors on pending applications on this work and are current employees of Corteva Agriscience™ which owns the pending patent applications. ZL, ST, MA, BL, TJ and NDC are current employees of Corteva Agriscience™.
Figures

References
-
- Afolabi, A.S. , Worland, B. , Snape, J.W. and Vain, P. (2004) A large‐scale study of rice plants transformed with different T‐DNAs provides new insights into locus composition and T‐DNA linkage configurations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 109, 815–826. - PubMed
-
- Akbudak, M.A. , More, A.B. , Nandy, S. and Srivastava, V. (2010) Dosage‐dependent gene expression from direct repeat locus in rice developed by site‐specific gene integration. Mol. Biotechnol. 45, 15–23. - PubMed
-
- Albert, H. , Dale, E.C. , Lee, E. and Ow, D.W. (1995) Site‐specific integration of DNA into wild‐type and mutant lox sites placed in the plant genome. Plant J. 7, 649–659. - PubMed
-
- Altpeter, F. , Baisakh, N. , Beachy, R. , Bock, R. , Capell, T. , Christou, P. , Daniell, H. et al. (2005) Particle bombardment and the genetic enhancement of crops: myths and realities. Mol. Breed. 15, 305–327.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

