Effects of prophylactic antibiotics before peritoneal dialysis catheter implantation on the clinical outcomes of peritoneal dialysis patients
- PMID: 30706749
- PMCID: PMC6366413
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2019.1568259
Effects of prophylactic antibiotics before peritoneal dialysis catheter implantation on the clinical outcomes of peritoneal dialysis patients
Abstract
Background: Peritoneal dialysis (PD) related infections, such as peritonitis, are still the main obstacle for the development of PD. Prophylactic antibiotic as one of the interventions to prevent early peritonitis was recommended to use before PD catheter insertion by International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis (ISPD) guidelines, In our hospital, however, since 2012, the prophylactic antibiotics for insertion of PD catheters were not allowed to use because of our hospital's regulation. In order to analyze the outcomes of PD patients without using prophylactic antibiotics before the PD catheter insertion, we compared the PD patients with or without prophylactic antibiotics before PD catheter insertion.
Methods: This retrospective study included 247 patients undergoing permanent PD catheter placement with conventional open surgical method consecutively between February 2008 and June 2013. Of these, 154 patients were given intravenous cefazolin, 1.0 g, 0.5-2 h before the procedure (antibiotic group) and 93 patients were not given prophylactic antibiotics (nonantibiotic group). All the patients were administered intermittent PD within 24 h after PD catheter insertion. The early complications and long-term outcomes were recorded respectively.
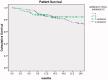
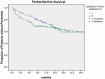
Results: There was no significant difference in the incidence of peritonitis and exit-site/tunnel infection and mechanical complications between the two groups in the first 30 days after the PD catheter implantation. In addition, after 6 years of follow-up, no difference was seen between the two groups in patient survival, technique survival, and peritonitis-free survival.
Conclusions: Our study does not show any beneficial effect of antibiotic prophylaxis in reducing the postoperative peritonitis.
Keywords: Peritoneal dialysis; antibiotics; peritoneal dialysis catheter; peritonitis; prophylaxis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intraperitoneal antibiotic administration for prevention of postoperative peritoneal catheter-related infections.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2018 Apr;22(2):448-452. doi: 10.1007/s10157-017-1476-8. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 28913721
-
Role of preoperative antibiotic prophylaxis in preventing postoperative peritonitis in newly placed peritoneal dialysis catheters.Am J Kidney Dis. 2000 Nov;36(5):1014-9. doi: 10.1053/ajkd.2000.19104. Am J Kidney Dis. 2000. PMID: 11054359 Clinical Trial.
-
Preoperative vancomycin prophylaxis for newly placed peritoneal dialysis catheters prevents postoperative peritonitis.Adv Perit Dial. 2000;16:199-203. Adv Perit Dial. 2000. PMID: 11045293 Clinical Trial.
-
Peritoneal Dialysis-Associated Peritonitis.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019 Jul 5;14(7):1100-1105. doi: 10.2215/CJN.14631218. Epub 2019 May 8. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31068338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial agents and catheter-related interventions to prevent peritonitis in peritoneal dialysis: Using evidence in the context of clinical practice.Int J Artif Organs. 2006 Jan;29(1):41-9. doi: 10.1177/039139880602900103. Int J Artif Organs. 2006. PMID: 16485238 Review.
References
-
- Tokgoz B. Clinical advantages of peritoneal dialysis. Perit Dial Int. 2009;29:S59–S61. - PubMed
-
- Morton RL, Tong A, Webster AC, et al. . Characteristics of dialysis important to patients and family caregivers: a mixed methods approach. Nephrol Dial Transplant.2011;26:4038–4046. - PubMed
-
- Bonifati C, Pansini F, Torres DD, et al. . Antimicrobial agents and catheter-related interventions to prevent peritonitis in peritoneal dialysis: using evidence in the context of clinical practice. Int J Artif Organs. 2006;29:41–49. - PubMed
-
- Diaz-Buxo JA. Modality selection. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998;9:S112–S117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical