Energy Expenditure and Enjoyment During Active Video Gaming Using an Adapted Wii Fit Balance Board in Adults with Physical Disabilities: Observational Study
- PMID: 30707098
- PMCID: PMC6376329
- DOI: 10.2196/11326
Energy Expenditure and Enjoyment During Active Video Gaming Using an Adapted Wii Fit Balance Board in Adults with Physical Disabilities: Observational Study
Abstract
Background: Individuals with physical disabilities have fewer opportunities to participate in enjoyable physical activity. One option for increasing physical activity is playing active video games (AVGs); however, many AVGs are inaccessible or offer limited play options.
Objective: This study aimed to examine energy expenditure and enjoyment in adults with mobility impairment during AVG play using off-the-shelf (OTS) and adapted versions of the Wii Fit balance board (Nintendo).
Methods: During visit 1, participants completed a functional assessment and the familiarization period. During visit 2, metabolic data were collected during a 20-minute baseline and four 10-minute bouts of Wii Fit Plus game play, with two bouts on each of the boards. During the resting period, participants completed the Physical Activity Enjoyment Scale (PACES). Statistical analyses were computed using SPSS software. Data were analyzed separately for individuals who were able to play while standing on both boards (StdStd); those who could not play while standing on the OTS board, but were able to play while standing on the adapted board (aStd); and those who could only play while sitting on the adapted board (aSit).
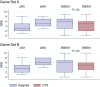
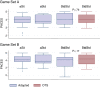
Results: Data were collected for 58 participants (StdStd, n=17; aStd, n=10; aSit, n=31). The sample included 31 men and 27 women with a mean age of 41.21 (SD 12.70) years. Energy expenditure (metabolic equivalent [MET]) during game play was significantly greater than that during rest for all players. Only 17 participants (StdStd group) were able to play using the OTS board. During game play on the adapted board, the average MET values for the two game sets were 2.261 (SD 0.718) kcal/kg/hour and 2.233 (SD 0.751) kcal/kg/hour for the aSit group, 3.151 (SD 1.034) and 2.990 (SD 1.121) for the aStd group, and 2.732 (SD 0.655) and 2.777 (SD 0.803) for the StdStd group. For game play on the adapted board, self-reported ratings of perceived exertion on a 0-10 scale suggested greater exercise intensity levels, with median scores ranging from moderate (3) to very hard (7). The PACES scores indicated that all players enjoyed using the adapted board, with a median score of 4 on a 5-point scale.
Conclusions: The adapted Wii Fit balance board provided an opportunity for individuals with mobility impairments, including wheelchair users, to engage in AVG. All participants were able to utilize the adapted controller and enjoyed the AVG activity. Although the average MET values achieved during AVG represented light-intensity exercise (<3 METs), 16% of sitting participants and 41% of standing participants achieved moderate-intensity exercise (3-6 METs) in at least one of the games. Factors not accounted for, which may have influenced the intensity of exercise, include game selection, limited familiarization period, and discomfort wearing the COSMED portable metabolic system for measurement of oxygen consumption. Accessible AVG controllers offer an innovative approach to overcome various barriers to participation in physical activity. The next steps include assessment of an AVG intervention using an adapted board gaming controller on health and fitness outcomes.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02994199; https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02994199 (Archived by Webcite at http://www.webcitation.org/75fc0mN39).
Keywords: disability; energy expenditure; enjoyment; exercise; exergaming; physical activity; video games.
©Laurie A Malone, Mohanraj Thirumalai, Sangeetha Padalabalanarayanan, Whitney N Neal, Sean Bowman, Tapan Mehta. Originally published in JMIR Serious Games (http://games.jmir.org), 01.02.2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Assessment of Active Video Gaming Using Adapted Controllers by Individuals With Physical Disabilities: A Protocol.JMIR Res Protoc. 2017 Jun 16;6(6):e116. doi: 10.2196/resprot.7621. JMIR Res Protoc. 2017. PMID: 28623186 Free PMC article.
-
Adapting the Wii Fit Balance Board to Enable Active Video Game Play by Wheelchair Users: User-Centered Design and Usability Evaluation.JMIR Rehabil Assist Technol. 2018 Mar 6;5(1):e2. doi: 10.2196/rehab.8003. JMIR Rehabil Assist Technol. 2018. PMID: 29510972 Free PMC article.
-
Active Video Gaming Using an Adapted Gaming Mat in Youth and Adults With Physical Disabilities: Observational Study.JMIR Serious Games. 2021 Aug 26;9(3):e30672. doi: 10.2196/30672. JMIR Serious Games. 2021. PMID: 34435962 Free PMC article.
-
A Narrative Synthesis of Nintendo Wii Fit Gaming Protocol in Addressing Balance Among Healthy Older Adults: What System Works?Games Health J. 2017 Apr;6(2):65-74. doi: 10.1089/g4h.2016.0082. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Games Health J. 2017. PMID: 28225644 Review.
-
Effect of Wii Fit Exercise With Balance and Lower Limb Muscle Strength in Older Adults: A Meta-Analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 May 6;9:812570. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.812570. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35602499 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Results and Guidelines From a Repeated-Measures Design Experiment Comparing Standing and Seated Full-Body Gesture-Based Immersive Virtual Reality Exergames: Within-Subjects Evaluation.JMIR Serious Games. 2020 Jul 27;8(3):e17972. doi: 10.2196/17972. JMIR Serious Games. 2020. PMID: 32716004 Free PMC article.
-
The Usability of a Touchpad Active Video Game Controller for Individuals With Impaired Mobility: Observational Study.JMIR Rehabil Assist Technol. 2023 Aug 3;10:e41993. doi: 10.2196/41993. JMIR Rehabil Assist Technol. 2023. PMID: 37535411 Free PMC article.
-
Development and initial validation of the German version of the Exergame Enjoyment Questionnaire (EEQ-G).PLoS One. 2023 Jun 8;18(6):e0286556. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286556. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37289701 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Evaluation of Intelligent Serious Games for Children With Learning Difficulties: Observational Study.JMIR Serious Games. 2020 Apr 16;8(2):e13190. doi: 10.2196/13190. JMIR Serious Games. 2020. PMID: 32297864 Free PMC article.
-
Usability of the GAIMplank Video Game Controller for People With Mobility Impairments: Observational Study.JMIR Serious Games. 2023 Jan 10;11:e38484. doi: 10.2196/38484. JMIR Serious Games. 2023. PMID: 36626195 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martin Ginis KA, Ma JK, Latimer-Cheung AE, Rimmer JH. A systematic review of review articles addressing factors related to physical activity participation among children and adults with physical disabilities. Health Psychol Rev. 2016 Dec;10(4):478–494. doi: 10.1080/17437199.2016.1198240. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rimmer JH, Padalabalanarayanan S, Malone LA, Mehta T. Fitness facilities still lack accessibility for people with disabilities. Disabil Health J. 2017 Dec;10(2):214–221. doi: 10.1016/j.dhjo.2016.12.011. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1936-6574(16)30186-8 S1936-6574(16)30186-8 - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

