Long noncoding RNA LINC00520 prevents the progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma through the inactivation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by downregulating EGFR
- PMID: 30707166
- PMCID: PMC6595718
- DOI: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000070
Long noncoding RNA LINC00520 prevents the progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma through the inactivation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by downregulating EGFR
Abstract
Background: Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) play pivotal roles in various malignant tumors. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling is associated with the pathogenesis of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC). This study aimed to explore the role of LINC00520 in the development of cSCC via EGFR and phosphoinositide 3-kinase-protein kinase B (PI3K/Akt) signaling pathways.
Methods: A microarray analysis was applied to screen differentially expressed lncRNAs in cSCC samples. The A431 cSCC cell line was transfected and assigned different groups. The expression patterns of LINC00520, EGFR, and intermediates in the PI3K/Akt pathway were characterized using reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and Western blotting analysis. Cell proliferation, migration, and invasion were detected using the MTT assay, scratch test, and Transwell assay, respectively. Cell-based experiments and a tumorigenicity assay were conducted to assess the effect of LINC00520 on cSCC progression. This study was ended in September 2017. Comparisons between two groups were analyzed with t-test and comparisons among multiple groups were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance. The nonparametric Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to analyze skewed data. The enumerated data were analyzed using the chi-square test or Fisher exact test.
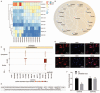
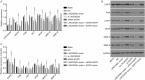
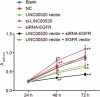
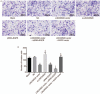
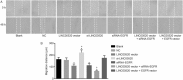
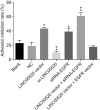
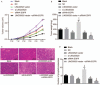
Results: Data from chip GSE66359 revealed depletion of LINC00520 in cSCC. Cells transfected with LINC00520 vector and LINC00520 vector + si-EGFR showed elevated LINC00520 level but decreased levels of the EGFR, PI3K, AKT, VEGF, MMP-2 and MMP-9 mRNAs and proteins, and inhibition of the growth, migration and adhesion of cSCC cells, while the si-LINC00520 group showed opposite trends (all P < 0.05). Compared with the LINC00520 vector group, the LINC00520 vector + si-EGFR group showed decreased levels of the EGFR, PI3K, AKT, VEGF, MMP-2 and MMP-9 mRNAs and proteins, and inhibition of the growth, migration and adhesion of cSCC cells, while the LINC00520 vector + EGFR vector group showed opposite results (all P < 0.05).
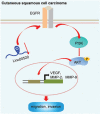
Conclusion: Based on our results, LINC00520-targeted EGFR inhibition might result in the inactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway, thus inhibiting cSCC development.
Figures
References
-
- Liu S, Chen M, Li P, Wu Y, Chang C, Qiu Y, et al. Ginsenoside rh2 inhibits cancer stem-like cells in skin squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem 2015; 36:499–508. doi: 10.1159/000430115. - PubMed
-
- Silberstein E, Sofrin E, Bogdanov-Berezovsky A, Nash M, Segal N. Lymph node metastasis in cutaneous head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Dermatol Surg 2015; 41:1126–1129. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000000488. - PubMed
-
- Mateus C. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Rev Prat 2014; 64:45–52. doi: 10.1016/j.cll.2017.06.003. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

