Tetrazoles via Multicomponent Reactions
- PMID: 30707567
- PMCID: PMC6376451
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00564
Tetrazoles via Multicomponent Reactions
Abstract
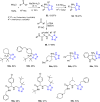
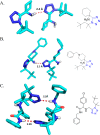
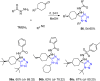
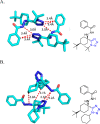
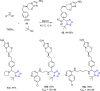
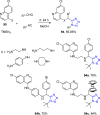
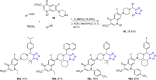
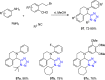
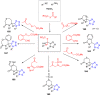
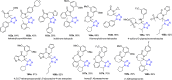
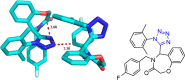
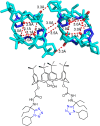
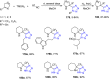
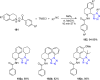
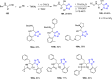
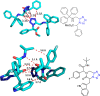
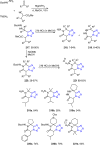
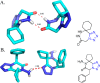
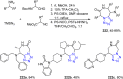
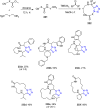
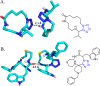
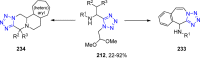
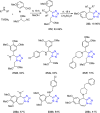
Tetrazole derivatives are a prime class of heterocycles, very important to medicinal chemistry and drug design due to not only their bioisosterism to carboxylic acid and amide moieties but also to their metabolic stability and other beneficial physicochemical properties. Although more than 20 FDA-approved drugs contain 1 H- or 2 H-tetrazole substituents, their exact binding mode, structural biology, 3D conformations, and in general their chemical behavior is not fully understood. Importantly, multicomponent reaction (MCR) chemistry offers convergent access to multiple tetrazole scaffolds providing the three important elements of novelty, diversity, and complexity, yet MCR pathways to tetrazoles are far from completely explored. Here, we review the use of multicomponent reactions for the preparation of substituted tetrazole derivatives. We highlight specific applications and general trends holding therein and discuss synthetic approaches and their value by analyzing scope and limitations, and also enlighten their receptor binding mode. Finally, we estimated the prospects of further research in this field.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
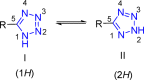
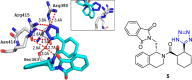
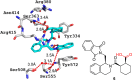
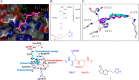
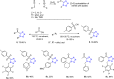
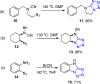
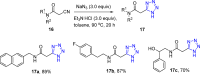
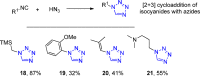
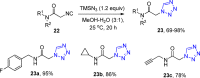
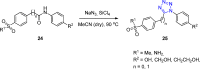
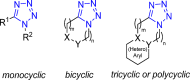
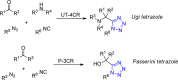
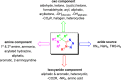
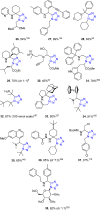
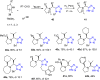
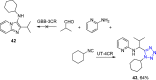
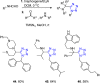
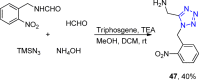
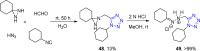
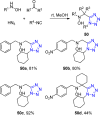
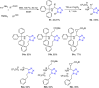
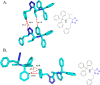
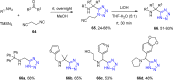
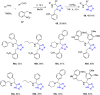
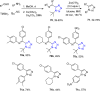
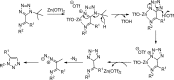
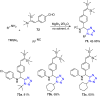
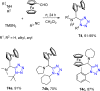
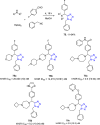
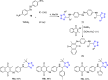
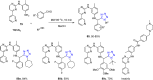
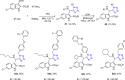
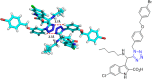
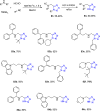
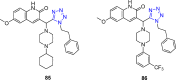
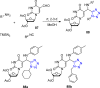
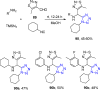
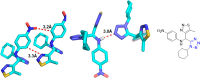
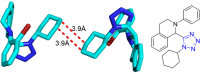
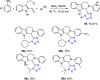
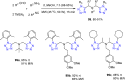
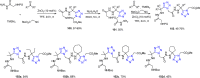
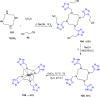
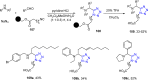
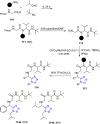
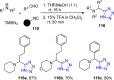

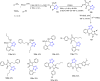

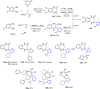
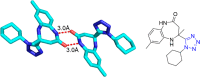
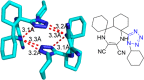
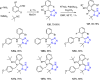
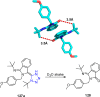
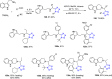
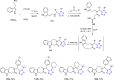
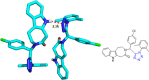
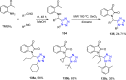
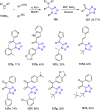
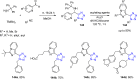
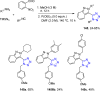
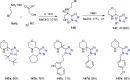
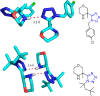
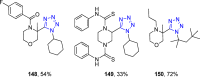
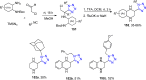
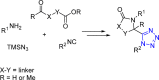
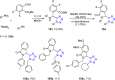
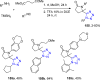
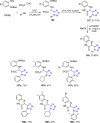
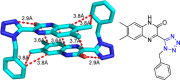
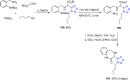
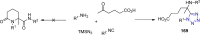
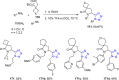
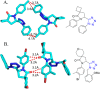
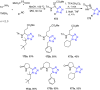
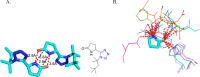
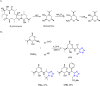
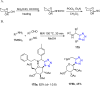
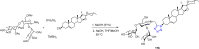
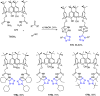
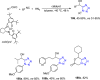
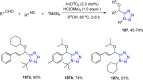
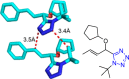
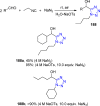
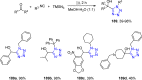

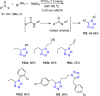
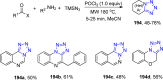
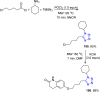
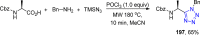
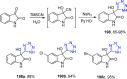
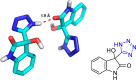
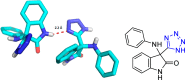
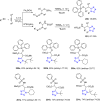
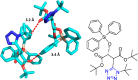
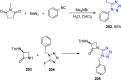
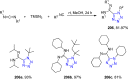
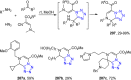
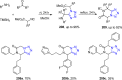
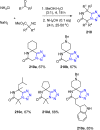
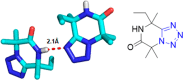
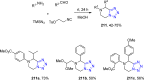
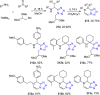
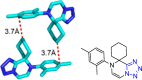
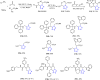
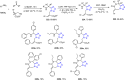
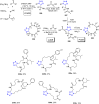
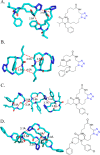
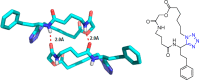
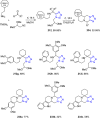
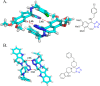
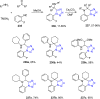
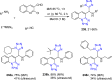
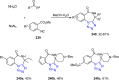
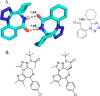

References
-
- Bhatt U.Five-Membered Heterocycles with Four Heteroatoms: Tetrazoles. In Modern Heterocyclic Chemistry; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 2011; pp 1401–1430.
-
- Bladin J. A. Ueber von Dicyanphenylhydrazin Abgeleitete Verbindungen. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1885, 18, 1544–1551. 10.1002/cber.188501801335. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

