Steroid biomarkers in human adrenal disease
- PMID: 30707926
- PMCID: PMC6707065
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.01.018
Steroid biomarkers in human adrenal disease
Abstract
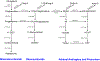
Adrenal steroidogenesis is a robust process, involving a series of enzymatic reactions that facilitate conversion of cholesterol into biologically active steroid hormones under the stimulation of angiotensin II, adrenocorticotropic hormone and other regulators. The biosynthesis of mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and adrenal-derived androgens occur in separate adrenocortical zones as a result of the segregated expression of steroidogenic enzymes and cofactors. This mini review provides the principles of adrenal steroidogenesis, including the classic and under-appreciated 11-oxygenated androgen pathways. Several adrenal diseases result from dysregulated adrenal steroid synthesis. Herein, we review growing evidence that adrenal diseases exhibit characteristic modifications from normal adrenal steroid pathways that provide opportunities for the discovery of biomarker steroids that would improve diagnosis and monitoring of adrenal disorders.
Keywords: Adrenal; Adrenal disease; Androgens; Biomarkers; Steroids.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Establishment of a Novel Human Fetal Adrenal Culture Model that Supports de Novo and Manipulated Steroidogenesis.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Mar 8;106(3):843-857. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa852. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33212489
-
Monogenic Disorders of Adrenal Steroidogenesis.Horm Res Paediatr. 2018;89(5):292-310. doi: 10.1159/000488034. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Horm Res Paediatr. 2018. PMID: 29874650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA regulation of adrenal glucocorticoid and androgen biosynthesis.Vitam Horm. 2024;124:1-37. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2023.06.006. Epub 2023 Nov 24. Vitam Horm. 2024. PMID: 38408797
-
Steroid profiling in adrenal disease.Clin Chim Acta. 2024 Jan 15;553:117749. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2023.117749. Epub 2023 Dec 31. Clin Chim Acta. 2024. PMID: 38169194 Review.
-
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Plasma and urinary steroid conjugates in seven children with steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency.Clin Chim Acta. 1973 Nov 15;48(4):359-65. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90413-0. Clin Chim Acta. 1973. PMID: 4761584 No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The Role of Biomarkers in Adrenocortical Carcinoma: A Review of Current Evidence and Future Perspectives.Biomedicines. 2021 Feb 10;9(2):174. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9020174. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33578890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update on adrenarche.Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020 Aug;32(4):574-581. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0000000000000928. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32692055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simultaneous steroids measurement in dogs with hyperadrenocorticism using a column-switching liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method.J Vet Med Sci. 2021 Oct 31;83(11):1634-1642. doi: 10.1292/jvms.21-0406. Epub 2021 Sep 17. J Vet Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34544959 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of sex and functional status on the value of serum steroid profiling in discriminating adrenocortical carcinoma from adrenocortical adenoma.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 18;15:1435102. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1435102. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39359414 Free PMC article.
-
Adrenal insufficiency.Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021 Mar 11;7(1):19. doi: 10.1038/s41572-021-00252-7. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021. PMID: 33707469 Review.
References
-
- Arnold J, Ein beitrag zu der feiner struktur und dem chemismus der nebennieren., Virchows Arch., 35 (1866) 64–107.
-
- Vinson GP, Adrenocortical zonation and ACTH, Microsc Res Tech, 61 (2003) 227–239. - PubMed
-
- Vinson GP, Ho MM, Origins of zonation: the adrenocortical model of tissue development and differentiation, Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol Suppl, 25 (1998) S91–96. - PubMed
-
- Hornsby PJ, Biosynthesis of DHEAS by the human adrenal cortex and its age-related decline, Ann N Y Acad Sci, 774 (1995) 29–46. - PubMed
-
- Parker LN, Odell WD, Control of adrenal androgen secretion, Endocr Rev, 1 (1980) 392–410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical