MicroRNA-144-3p targets relaxin/insulin-like family peptide receptor 1 (RXFP1) expression in lung fibroblasts from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 30709904
- PMCID: PMC6442041
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004910
MicroRNA-144-3p targets relaxin/insulin-like family peptide receptor 1 (RXFP1) expression in lung fibroblasts from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
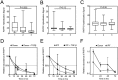
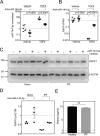
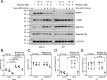
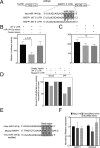
The hormone relaxin is considered a potential therapy for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). We have previously shown that a potential limitation to relaxin-based IPF therapy is decreased expression of a relaxin receptor, relaxin/insulin-like family peptide receptor 1 (RXFP1), in IPF fibroblasts. The mechanism that down-regulates RXFP1 in IPF remains unclear. To determine whether microRNAs (miRs) regulate RXFP1 gene expression, here we employed a bioinformatics approach to identify miRs predicted to target RXFP1 and identified a putative miR-144-3p target site in the RXFP1 mRNA. In situ hybridization of IPF lung biopsies revealed that miR-144-3p is expressed in fibroblastic foci. Furthermore, we found that miR-144-3p is up-regulated in IPF fibroblasts compared with lung fibroblasts from healthy donors. Transforming growth factor β increased miR-144-3p expression in both healthy and IPF lung fibroblasts in a SMAD family 2/3 (SMAD2/3)-dependent manner, and Jun proto-oncogene AP-1 transcription factor subunit (AP-1) was required for constitutive miR-144-3p expression. Overexpression of an miR-144-3p mimic significantly reduced RXFP1 mRNA and protein levels and increased expression of the myofibroblast marker α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) in healthy lung fibroblasts. IPF lung fibroblasts transfected with anti-miR-144-3p had increased RXFP1 expression and reduced α-SMA expression. Of note, a lentiviral luciferase reporter carrying the WT 3' UTR of RXFP1 was significantly repressed in IPF lung fibroblasts, whereas a reporter carrying a mutated miR-144-3p-binding site exhibited less sensitivity toward endogenous miR-144-3p expression, indicating that miR-144-3p down-regulates RXFP1 in IPF lung fibroblasts by targeting its 3' UTR. We conclude that miR-144-3p directly represses RXFP1 mRNA and protein expression.
Keywords: epigenetics; fibroblast; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; lung disease; lung fibroblasts; miR-144-3p; microRNA (miRNA); myofibroblast; post-transcriptional regulation; pulmonary fibrosis; relaxin; relaxin/insulin-like family peptide receptor 1 (RXFP1); transforming growth factor β (TGF-B).
© 2019 Bahudhanapati et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures






Similar articles
-
Expression of RXFP1 Is Decreased in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Implications for Relaxin-based Therapies.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016 Dec 1;194(11):1392-1402. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201509-1865OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016. PMID: 27310652 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a distal RXFP1 gene enhancer with differential activity in fibrotic lung fibroblasts involving AP-1.PLoS One. 2021 Dec 31;16(12):e0254466. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254466. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34972106 Free PMC article.
-
miR-130b-3p Modulates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Crosstalk in Lung Fibrosis by Targeting IGF-1.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 8;11(3):e0150418. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150418. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26953888 Free PMC article.
-
The relaxin family peptide receptor 1 (RXFP1): An emerging player in human health and disease.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020 Apr;8(4):e1194. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1194. Epub 2020 Feb 26. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020. PMID: 32100955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Transl Res. 2011 Apr;157(4):191-9. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2011.01.012. Epub 2011 Feb 4. Transl Res. 2011. PMID: 21420029 Review.
Cited by
-
Revisiting the role of MicroRNAs in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Oct 16;12:1470875. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1470875. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39479511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Delivery and Gene Therapy in Pulmonary Hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 25;22(3):1179. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031179. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33503992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
circGRHPR inhibits aberrant epithelial-mesenchymal transformation progression of lung epithelial cells associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 Jan 25;40(1):7. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09839-8. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38267743 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulating ANGPTL3 by miR-144-3p promoted TGF-β1-induced renal interstitial fibrosis via activating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 8;10(3):e24204. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24204. eCollection 2024 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38322878 Free PMC article.
-
A Six-Gene Signature Predicts Survival of Adenocarcinoma Type of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Comprehensive Study Based on Integrated Analysis and Weighted Gene Coexpression Network.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Dec 4;2019:4250613. doi: 10.1155/2019/4250613. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31886214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raghu G., Lynch D., Godwin J. D., Webb R., Colby T. V., Leslie K. O., Behr J., Brown K. K., Egan J. J., Flaherty K. R., Martinez F. J., Wells A. U., Shao L., Zhou H., Pedersen P. S., et al. (2014) Diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with high-resolution CT in patients with little or no radiological evidence of honeycombing: secondary analysis of a randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2, 277–284 10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70011-6 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

