The expanding roles and mechanisms of G protein-mediated presynaptic inhibition
- PMID: 30710014
- PMCID: PMC6364771
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.TM118.004163
The expanding roles and mechanisms of G protein-mediated presynaptic inhibition
Abstract
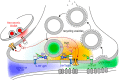
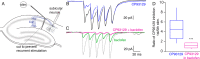
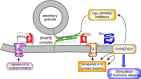
Throughout the past five decades, tremendous advancements have been made in our understanding of G protein signaling and presynaptic inhibition, many of which were published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry under the tenure of Herb Tabor as Editor-in-Chief. Here, we identify these critical advances, including the formulation of the ternary complex model of G protein-coupled receptor signaling and the discovery of Gβγ as a critical signaling component of the heterotrimeric G protein, along with the nature of presynaptic inhibition and its physiological role. We provide an overview for the discovery and physiological relevance of the two known Gβγ-mediated mechanisms for presynaptic inhibition: first, the action of Gβγ on voltage-gated calcium channels to inhibit calcium influx to the presynaptic active zone and, second, the direct binding of Gβγ to the SNARE complex to displace synaptotagmin downstream of calcium entry, which has been demonstrated to be important in neurons and secretory cells. These two mechanisms act in tandem with each other in a synergistic manner to provide more complete spatiotemporal control over neurotransmitter release.
Keywords: G protein; G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR); SNARE proteins; neuroscience; pharmacology.
© 2019 Zurawski et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
References
-
- Tsai B. S., and Lefkowitz R. J. (1979) Agonist-specific effects of guanine nucleotides on α-adrenergic receptors in human platelets. Mol. Pharmacol. 16, 61–68 - PubMed
-
- Maguire M. E., Van Arsdale P. M., and Gilman A. G. (1976) An agonist-specific effect of guanine nucleotides on binding to the β adrenergic receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 12, 335–339 - PubMed
-
- Lefkowitz R. J., Mullikin D., and Caron M. G. (1976) Regulation of β-adrenergic receptors by guanyl-5′-yl imidodiphosphate and other purine nucleotides. J. Biol. Chem. 251, 4686–4692 - PubMed
-
- Stadel J. M., DeLean A., and Lefkowitz R. J. (1980) A high affinity agonist-β-adrenergic receptor complex is an intermediate for catecholamine stimulation of adenylate cyclase in turkey and frog erythrocyte membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 255, 1436–1441 - PubMed
-
- Lucas M., and Bockaert J. (1977) Use of (−)-[3H]dihydroalprenolol to study β adrenergic receptor-adenylate cyclase coupling in C6 glioma cells: role of 5′-guanylylimidodiphosphate. Mol. Pharmacol. 13, 314–329 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

