Nonceliac Wheat Sensitivity: An Immune-Mediated Condition with Systemic Manifestations
- PMID: 30711208
- PMCID: PMC6364564
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gtc.2018.09.012
Nonceliac Wheat Sensitivity: An Immune-Mediated Condition with Systemic Manifestations
Abstract
Non-celiac wheat sensitivity (NCWS) is characterized by gastrointestinal and extra-intestinal symptoms following the ingestion of gluten-containing cereals in subjects without celiac disease or wheat allergy. The identity of the molecular triggers in these cereals responsible for the symptoms of NCWS remains to be delineated. Recent research has identified a biological basis for the condition, with the observation of systemic immune activation in response to microbial translocation that appears to be linked to intestinal barrier defects. Ongoing research efforts are aimed at further characterizing the etiology, mechanism, and biomarkers of the condition.
Keywords: Amylase/protease inhibitor; Antibody to native gliadin; Biomarkers; Fructan; Gluten; Intestinal barrier function; Systemic immune activation; Wheat.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
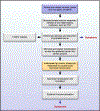
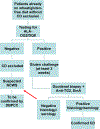

References
-
- Leonard MM, Sapone A, Catassi C, et al. Celiac disease and nonceliac gluten sensitivity: a review. JAMA 2017;318:647–56. - PubMed
-
- Lebwohl B, Sanders DS, Green PHR. Coeliac disease. Lancet. 2018;391:70–81. - PubMed
-
- Volta U, De Giorgio R. New understanding of gluten sensitivity. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;9:295–9. - PubMed
-
- (Lebwohl Ludvigsson et al. 2015).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

