miR-132-3p is a positive regulator of alpha-cell mass and is downregulated in obese hyperglycemic mice
- PMID: 30711402
- PMCID: PMC6437597
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.01.004
miR-132-3p is a positive regulator of alpha-cell mass and is downregulated in obese hyperglycemic mice
Abstract
Objective: Diabetes is a complex disease implicating several organs and cell types. Within the islets, dysregulation occurs in both alpha- and beta-cells, leading to defects of insulin secretion and increased glucagon secretion. Dysregulation of alpha-cells is associated with transcriptome changes. We hypothesized that microRNAs (miRNAs) which are negative regulators of mRNA stability and translation could be involved in alpha-cell alterations or adaptations during type 2 diabetes.
Methods: miRNA microarray analyses were performed on pure alpha- and beta-cells from high-fat diet fed obese hyperglycemic mice and low-fat diet fed controls. Then, the most regulated miRNA was overexpressed or inhibited in primary culture of mouse and human alpha-cells to determine its molecular and functional impact.
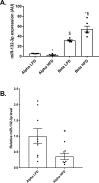
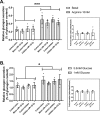
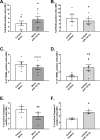
Results: 16 miRNAs were significantly regulated in alpha-cells of obese hyperglycemic mice and 28 in beta-cells. miR-132-3p had the strongest regulation level in alpha-cells, where it was downregulated, while we observed an opposite upregulation in beta-cells. In vitro experiments showed that miR-132-3p, which is inversely regulated by somatostatin and cAMP, is a positive modulator of alpha-cell proliferation and implicated in their resistance to apoptosis. These effects are associated with the regulation of a series of genes, including proliferation and stress markers Mki67 and Bbc3 in mouse and human alpha-cells, potentially involved in miR-132-3p functions.
Conclusions: Downregulation of miR-132-3p in alpha-cells of obese diabetic mice may constitute a compensatory mechanism contributing to keep glucagon-producing cell number constant in diabetes.
Keywords: Alpha-cell; Apoptosis; Glucagon; Proliferation; Type 2 diabetes; miR-132-3p.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier GmbH.. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Dunning B.E., Foley J.E., Ahren B. Alpha cell function in health and disease: influence of glucagon-like peptide-1. Diabetologia. 2005;48:1700–1713. - PubMed
-
- Gromada J., Franklin I., Wollheim C.B. Alpha-cells of the endocrine pancreas: 35 years of research but the enigma remains. Endocrine Reviews. 2007;28:84–116. - PubMed
-
- Quesada I., Tuduri E., Ripoll C., Nadal A. Physiology of the pancreatic alpha-cell and glucagon secretion: role in glucose homeostasis and diabetes. Journal of Endocrinology. 2008;199:5–19. - PubMed
-
- Gosmain Y., Avril I., Mamin A., Philippe J. Pax-6 and c-Maf functionally interact with the alpha-cell-specific DNA element G1 in vivo to promote glucagon gene expression. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2007;282:35024–35034. - PubMed
-
- Heddad Masson M., Poisson C., Guerardel A., Mamin A., Philippe J., Gosmain Y. Foxa1 and Foxa2 regulate alpha-cell differentiation, glucagon biosynthesis, and secretion. Endocrinology. 2014;155:3781–3792. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

