Micro-RNAs secreted through astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles cause neuronal network degeneration in C9orf72 ALS
- PMID: 30711519
- PMCID: PMC6413467
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.11.067
Micro-RNAs secreted through astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles cause neuronal network degeneration in C9orf72 ALS
Abstract
Background: Astrocytes regulate neuronal function, synaptic formation and maintenance partly through secreted extracellular vesicles (EVs). In amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) astrocytes display a toxic phenotype that contributes to motor neuron (MN) degeneration.
Methods: We used human induced astrocytes (iAstrocytes) from 3 ALS patients carrying C9orf72 mutations and 3 non-affected donors to investigate the role of astrocyte-derived EVs (ADEVs) in ALS astrocyte toxicity. ADEVs were isolated from iAstrocyte conditioned medium via ultracentrifugation and resuspended in fresh astrocyte medium before testing ADEV impact on HB9-GFP+ mouse motor neurons (Hb9-GFP+ MN). We used post-mortem brain and spinal cord tissue from 3 sporadic ALS and 3 non-ALS cases for PCR analysis.
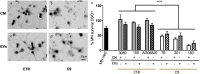
Findings: We report that EV formation and miRNA cargo are dysregulated in C9ORF72-ALS iAstrocytes and this affects neurite network maintenance and MN survival in vitro. In particular, we have identified downregulation of miR-494-3p, a negative regulator of semaphorin 3A (SEMA3A) and other targets involved in axonal maintenance. We show here that by restoring miR-494-3p levels through expression of an engineered miRNA mimic we can downregulate Sema3A levels in MNs and increases MN survival in vitro. Consistently, we also report lower levels of mir-494-3p in cortico-spinal tract tissue isolated from sporadic ALS donors, thus supporting the pathological importance of this pathway in MNs and its therapeutic potential.
Interpretation: ALS ADEVs and their miRNA cargo are involved in MN death in ALS and we have identified miR-494-3p as a potential therapeutic target.
Funding: Thierry Latran Fondation and Academy of Medical Sciences.
Keywords: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; Astrocytes; Axonal growth; Extracelular vesicles; Gene therapy; Neurodegeneration; miRNA.
Crown Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Fischer L.R., Culver D.G., Tennant P. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is a distal axonopathy: evidence in mice and man. Exp Neurol. 2004;185(2):232–240. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

