Regional Activation of Myosin II in Cancer Cells Drives Tumor Progression via a Secretory Cross-Talk with the Immune Microenvironment
- PMID: 30712866
- PMCID: PMC6370915
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.12.038
Regional Activation of Myosin II in Cancer Cells Drives Tumor Progression via a Secretory Cross-Talk with the Immune Microenvironment
Abstract
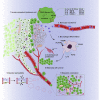
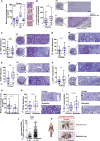
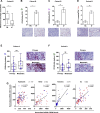
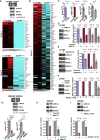
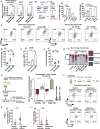
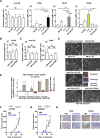
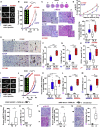
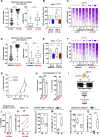
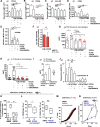
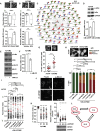
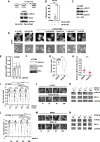
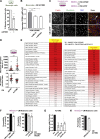
ROCK-Myosin II drives fast rounded-amoeboid migration in cancer cells during metastatic dissemination. Analysis of human melanoma biopsies revealed that amoeboid melanoma cells with high Myosin II activity are predominant in the invasive fronts of primary tumors in proximity to CD206+CD163+ tumor-associated macrophages and vessels. Proteomic analysis shows that ROCK-Myosin II activity in amoeboid cancer cells controls an immunomodulatory secretome, enabling the recruitment of monocytes and their differentiation into tumor-promoting macrophages. Both amoeboid cancer cells and their associated macrophages support an abnormal vasculature, which ultimately facilitates tumor progression. Mechanistically, amoeboid cancer cells perpetuate their behavior via ROCK-Myosin II-driven IL-1α secretion and NF-κB activation. Using an array of tumor models, we show that high Myosin II activity in tumor cells reprograms the innate immune microenvironment to support tumor growth. We describe an unexpected role for Myosin II dynamics in cancer cells controlling myeloid function via secreted factors.
Keywords: NF-κB; ROCK-Myosin II; macrophages; protein secretion; rounded-amoeboid melanoma cells; tumor invasive front.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Amano M., Ito M., Kimura K., Fukata Y., Chihara K., Nakano T., Matsuura Y., Kaibuchi K. Phosphorylation and activation of myosin by Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase) J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:20246–20249. - PubMed
-
- Avery-Kiejda K.A., Bowden N.A., Croft A.J., Scurr L.L., Kairupan C.F., Ashton K.A., Talseth-Palmer B.A., Rizos H., Zhang X.D., Scott R.J., Hersey P. P53 in human melanoma fails to regulate target genes associated with apoptosis and the cell cycle and may contribute to proliferation. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:203. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- C48390/A21153/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 14257/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 16-1135/AICR_/Worldwide Cancer Research/United Kingdom
- 12065/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- FC001112/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- FC001112/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- FC001112/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MR/L023091/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 24478/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 21153/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C10355/A15587/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- IS-BRC-1215-20006/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- C33043/A24478/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C30122/A15774/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C30122/A11527/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

