Endogenously Expressed Antigens Bind Mammalian RNA via Cationic Domains that Enhance Priming of Effector CD8 T Cells by DNA Vaccination
- PMID: 30713086
- PMCID: PMC6403493
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.01.011
Endogenously Expressed Antigens Bind Mammalian RNA via Cationic Domains that Enhance Priming of Effector CD8 T Cells by DNA Vaccination
Abstract
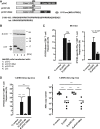
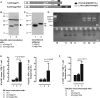
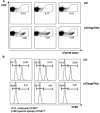
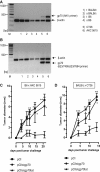
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) core (HBV-C) antigens with homologous or heterologous HIV-tat48-57-like (HBV-C149tat) cationic domains non-specifically bind cellular RNA in vector-transfected cells. Here, we investigated whether RNA-binding to cationic domains influences the immunogenicity of endogenously expressed antigens delivered by DNA vaccination. We initially evaluated induction of HBV-C (Kb/C93)-specific CD8+ T cell responses in C57BL/6J (B6) and 1.4HBV-Smut transgenic (tg) mice that harbor a replicating HBV genome in hepatocytes by DNA immunization. RNA-binding HBV-C and HBV-C149tat antigens moderately enhanced Kb/C93-specific CD8+ T cells in B6 mice as compared with RNA-free HBV-C149 antigen (lacking cationic domains). However, only the RNA-binding antigens elicited Kb/C93-specific CD8+ T cells that inhibited HBV replication in 1.4HBV-Smut tg mice. Moreover, RNA-binding to designer antigens, which express a Kb/p15E epitope from an endogenous murine leukemia virus-derived tumor-specific gp70 protein, was crucial to prime tumor-rejecting effector CD8+ T cells in B6 mice. Antigen-bound endogenous RNAs function as a Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR-7) ligand and stimulated priming of Kb/p15E-specific CD8+ T cells in B6, but not TLR-7-/-, mice. Antigen-bound cellular RNAs thus function as an endogenous natural adjuvant in in vivo vector-transfected cells, and thus are an attractive tool to induce and/or enhance effector CD8+ T cell responses directed against chronic viral infections or tumor self-antigens by DNA vaccination.
Keywords: CD8 T cells; DNA vaccination; RNA-binding; adjuvant; cationic domains.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cationic domains in particle-forming and assembly-deficient HBV core antigens capture mammalian RNA that stimulates Th1-biased antibody responses by DNA vaccination.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 2;8(1):14660. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32971-5. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30279478 Free PMC article.
-
Elimination of immunodominant epitopes from multispecific DNA-based vaccines allows induction of CD8 T cells that have a striking antiviral potential.J Immunol. 2009 Jul 1;183(1):370-80. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900505. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19542448
-
Differential presentation of endogenous and exogenous hepatitis B surface antigens influences priming of CD8(+) T cells in an epitope-specific manner.Eur J Immunol. 2014 Jul;44(7):1981-91. doi: 10.1002/eji.201343933. Epub 2014 May 11. Eur J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24723392
-
A tumor-specific neoepitope expressed in homologous/self or heterologous/viral antigens induced comparable effector CD8+ T-cell responses by DNA vaccination.Vaccine. 2020 May 6;38(21):3711-3719. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.04.003. Epub 2020 Apr 9. Vaccine. 2020. PMID: 32278524
-
Praziquantel facilitates IFN-γ-producing CD8+ T cells (Tc1) and IL-17-producing CD8+ T cells (Tc17) responses to DNA vaccination in mice.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e25525. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025525. Epub 2011 Oct 5. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21998665 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
IFN-γ treatment protocol for MHC-Ilo/PD-L1+ pancreatic tumor cells selectively restores their TAP-mediated presentation competence and CD8 T-cell priming potential.J Immunother Cancer. 2020 Aug;8(2):e000692. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-000692. J Immunother Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32868392 Free PMC article.
-
PreS1 Containing HBc VLPs for the Development of a Combined Therapeutic/Prophylactic Hepatitis B Vaccine.Microorganisms. 2023 Apr 8;11(4):972. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11040972. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37110395 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombospondin 2/Toll-Like Receptor 4 Axis Contributes to HIF-1α-Derived Glycolysis in Colorectal Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Nov 10;10:557730. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.557730. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33244454 Free PMC article.
-
Immunization with GP1 but Not Core-like Particles Displaying Isolated Receptor-Binding Epitopes Elicits Virus-Neutralizing Antibodies against Junín Virus.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Jan 22;10(2):173. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10020173. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35214632 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Riedl P., Stober D., Oehninger C., Melber K., Reimann J., Schirmbeck R. Priming Th1 immunity to viral core particles is facilitated by trace amounts of RNA bound to its arginine-rich domain. J. Immunol. 2002;168:4951–4959. - PubMed
-
- Fotin-Mleczek M., Duchardt K.M., Lorenz C., Pfeiffer R., Ojkić-Zrna S., Probst J., Kallen K.J. Messenger RNA-based vaccines with dual activity induce balanced TLR-7 dependent adaptive immune responses and provide antitumor activity. J. Immunother. 2011;34:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Sominskaya I., Skrastina D., Petrovskis I., Dishlers A., Berza I., Mihailova M., Jansons J., Akopjana I., Stahovska I., Dreilina D. A VLP library of C-terminally truncated Hepatitis B core proteins: correlation of RNA encapsidation with a Th1/Th2 switch in the immune responses of mice. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e75938. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Heidenreich R., Jasny E., Kowalczyk A., Lutz J., Probst J., Baumhof P., Scheel B., Voss S., Kallen K.J., Fotin-Mleczek M. A novel RNA-based adjuvant combines strong immunostimulatory capacities with a favorable safety profile. Int. J. Cancer. 2015;137:372–384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

