A Patient with a Benign and a Malignant Primary Pulmonary Meningioma: An Evaluation with 18F Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography and Computed Tomography with Iodinated Contrast
- PMID: 30713380
- PMCID: PMC6352649
- DOI: 10.4103/ijnm.IJNM_101_18
A Patient with a Benign and a Malignant Primary Pulmonary Meningioma: An Evaluation with 18F Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography and Computed Tomography with Iodinated Contrast
Abstract
An 80-year-old male with a previous history of thymoma and kidney cancer underwent a 18F fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET)/contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scan: two pulmonary nodules were discovered, both characterized by an increased glucose uptake. Of them, only one showed mild contrast enhancement. Both nodules were surgically resected: the first nodule was a benign meningioma and the second one was a malignant meningioma. This case study shows that malignancy of meningioma in the lung is not correlated with 18F FDG uptake and the contrast enhancement, thus suggesting that PET/CT may represent a suboptimal imaging modality for the evaluation of these lesions.
Keywords: 18F fluorodeoxyglucose; ectopic meningioma; iodinated contrast enhancement; malignant meningioma; pulmonary nodule.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
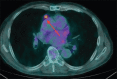
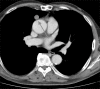

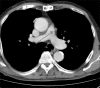
References
-
- Kim YY, Hong YK, Kie JH, Ryu SJ. Primary pulmonary meningioma: An unusual cause of a nodule with strong and homogeneous enhancement. Clin Imaging. 2016;40:170–3. - PubMed
-
- Kemnitz P, Spormann H, Heinrich P. Meningioma of lung: First report with light and electron microscopic findings. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1982;3:359–65. - PubMed
-
- Caobelli F, Facchetti F, Pizzocaro C, Ferrari V, Savelli G, Guerra UP, et al. A very unusual and aggressive form of a primary pulmonary meningioma seen with a 68Ga-DOTATOC PET/CT image. Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2015;34:123–4. - PubMed

