Charge Transfer between [4Fe4S] Proteins and DNA Is Unidirectional: Implications for Biomolecular Signaling
- PMID: 30714018
- PMCID: PMC6350243
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chempr.2018.09.026
Charge Transfer between [4Fe4S] Proteins and DNA Is Unidirectional: Implications for Biomolecular Signaling
Erratum in
-
Correction: Charge Transfer between [4Fe4S] Proteins and DNA Is Unidirectional: Implications for Biomolecular Signaling.Chem. 2019 Jun 13;5(6):1682-1684. doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2019.05.016. Chem. 2019. PMID: 31363507 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Recent experiments suggest that DNA-mediated charge transport might enable signaling between the [4Fe4S] clusters in the C-terminal domains of human DNA primase and polymerase α, as well as the signaling between other replication and repair high-potential [4Fe4S] proteins. Our theoretical study demonstrates that the redox signaling cannot be accomplished exclusively by DNA-mediated charge transport because part of the charge transfer chain has an unfavorable free energy profile. We show that hole or excess electron transfer between a [4Fe4S] cluster and a nucleic acid duplex through a protein medium can occur within microseconds in one direction, while it is kinetically hindered in the opposite direction. We present a set of signaling mechanisms that may occur with the assistance of oxidants or reductants, using the allowed charge transfer processes. These mechanisms would enable the coordinated action of [4Fe4S] proteins on DNA, engaging the [4Fe4S] oxidation state dependence of the protein-DNA binding affinity.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
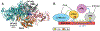
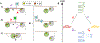
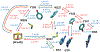
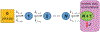
References
-
- Roche B, Aussel L, Ezraty B, Mandin P, Py B, and Barras F (2013) Iron/sulfur proteins biogenesis in prokaryotes: Formation, regulation and diversity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg 1827, 455–469. - PubMed
-
- Rouault TA (2015) Mammalian iron-sulphur proteins: novel insights into biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 16, 45–55. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
