Topical and Transdermal Drug Delivery: From Simple Potions to Smart Technologies
- PMID: 30714524
- PMCID: PMC6637104
- DOI: 10.2174/1567201816666190201143457
Topical and Transdermal Drug Delivery: From Simple Potions to Smart Technologies
Abstract
This overview on skin delivery considers the evolution of the principles of percutaneous absorption and skin products from ancient times to today. Over the ages, it has been recognised that products may be applied to the skin for either local or systemic effects. As our understanding of the anatomy and physiology of the skin has improved, this has facilitated the development of technologies to effectively and quantitatively deliver solutes across this barrier to specific target sites in the skin and beyond. We focus on these technologies and their role in skin delivery today and in the future.
Keywords: History; follicular transport; microneedles; minimally invasive; nanotechnology; physical enhancement; skin delivery; stratum corneum; targeted delivery; transdermal technologies; wearable devices..
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Figures

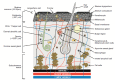



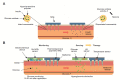
References
-
- Geller M.J. Ancient Babylonian medicine. Malden: Wiley-Blackwell; 2010.
-
- Selwyn S. The topical treatment of skin infection. In: Maibach H.I., Aly R., editors. Skin Microbiology. Relevance to Clinical Infection. New York: Springer-Verlag; 1981. pp. 317–328.
-
- Ebbell B. The Papyrus Ebers: the greatest Egyptian medical document. Copenhagen: Levin & Munksgaard; 1937.
-
- Moghimi H.R., Shafizade A., Kamlinejad M. Drug delivery systems in Iranian traditional pharmacy (in Persian). Traditional Medicine and Materia Medica Research Center, SBMU, Tehran, Iran: 2011.
-
- Morgan W.F. Poisoning by the external application of belladonna. BMJ. 1866;2:621.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

