Micro-/Nanorobots Propelled by Oscillating Magnetic Fields
- PMID: 30715039
- PMCID: PMC6266240
- DOI: 10.3390/mi9110540
Micro-/Nanorobots Propelled by Oscillating Magnetic Fields
Abstract
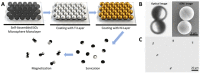
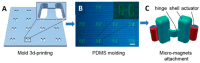
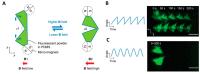
Recent strides in micro- and nanomanufacturing technologies have sparked the development of micro-/nanorobots with enhanced power and functionality. Due to the advantages of on-demand motion control, long lifetime, and great biocompatibility, magnetic propelled micro-/nanorobots have exhibited considerable promise in the fields of drug delivery, biosensing, bioimaging, and environmental remediation. The magnetic fields which provide energy for propulsion can be categorized into rotating and oscillating magnetic fields. In this review, recent developments in oscillating magnetic propelled micro-/nanorobot fabrication techniques (such as electrodeposition, self-assembly, electron beam evaporation, and three-dimensional (3D) direct laser writing) are summarized. The motion mechanism of oscillating magnetic propelled micro-/nanorobots are also discussed, including wagging propulsion, surface walker propulsion, and scallop propulsion. With continuous innovation, micro-/nanorobots can become a promising candidate for future applications in the biomedical field. As a step toward designing and building such micro-/nanorobots, several types of common fabrication techniques are briefly introduced. Then, we focus on three propulsion mechanisms of micro-/nanorobots in oscillation magnetic fields: (1) wagging propulsion; (2) surface walker; and (3) scallop propulsion. Finally, a summary table is provided to compare the abilities of different micro-/nanorobots driven by oscillating magnetic fields.
Keywords: fabrication techniques; micro-/nanorobots; oscillating magnetic fields; propulsion mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Magnetically Driven Micro and Nanorobots.Chem Rev. 2021 Apr 28;121(8):4999-5041. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c01234. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Chem Rev. 2021. PMID: 33787235 Free PMC article.
-
Micro/nanorobots for precise drug delivery via targeted transport and triggered release: A review.Int J Pharm. 2022 Mar 25;616:121551. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121551. Epub 2022 Feb 5. Int J Pharm. 2022. PMID: 35131352 Review.
-
Micro/Nanorobot: A Promising Targeted Drug Delivery System.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Jul 15;12(7):665. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12070665. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32679772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Self-Propelled Janus Microdimer Swimmers under a Rotating Magnetic Field.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019 Nov 22;9(12):1672. doi: 10.3390/nano9121672. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31771115 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Control of the Magnetically Actuated Micro/Nanorobot Swarm toward Biomedical Applications.Adv Healthc Mater. 2024 Jun;13(15):e2400414. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202400414. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024. PMID: 38412402 Review.
Cited by
-
Bio-Inspired Micro- and Nanorobotics Driven by Magnetic Field.Materials (Basel). 2022 Nov 4;15(21):7781. doi: 10.3390/ma15217781. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36363368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In-Silico Conceptualisation of Continuous Millifluidic Separators for Magnetic Nanoparticles.Materials (Basel). 2021 Nov 4;14(21):6635. doi: 10.3390/ma14216635. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34772161 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering microrobots for targeted cancer therapies from a medical perspective.Nat Commun. 2020 Nov 5;11(1):5618. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19322-7. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33154372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances of medical nanorobots for future cancer treatments.J Hematol Oncol. 2023 Jul 14;16(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01463-z. J Hematol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37452423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transnasal targeted delivery of therapeutics in central nervous system diseases: a narrative review.Front Neurosci. 2023 May 19;17:1137096. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1137096. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37292158 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Palagi S., Fischer P. Bioinspired microrobots. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018;3:113–124. doi: 10.1038/s41578-018-0016-9. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 51705108/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 91648201/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 51675140/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 51875141/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2016KM004/Key Laboratory of Micro-systems and Microstructures Manufacturing of Ministry of Education
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

