Sex Differences in the Association of Global Amyloid and Regional Tau Deposition Measured by Positron Emission Tomography in Clinically Normal Older Adults
- PMID: 30715078
- PMCID: PMC6515599
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.4693
Sex Differences in the Association of Global Amyloid and Regional Tau Deposition Measured by Positron Emission Tomography in Clinically Normal Older Adults
Abstract
Importance: Mounting evidence suggests that sex differences exist in the pathologic trajectory of Alzheimer disease. Previous literature shows elevated levels of cerebrospinal fluid tau in women compared with men as a function of apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 status and β-amyloid (Aβ). What remains unclear is the association of sex with regional tau deposition in clinically normal individuals.
Objective: To examine sex differences in the cross-sectional association between Aβ and regional tau deposition as measured with positron emission tomography (PET).
Design, setting and participants: This is a study of 2 cross-sectional, convenience-sampled cohorts of clinically normal individuals who received tau and Aβ PET scans. Data were collected between January 2016 and February 2018 from 193 clinically normal individuals from the Harvard Aging Brain Study (age range, 55-92 years; 118 women [61%]) who underwent carbon 11-labeled Pittsburgh Compound B and flortaucipir F18 PET and 103 clinically normal individuals from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (age range, 63-94 years; 55 women [51%]) who underwent florbetapir and flortaucipir F 18 PET.
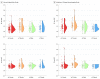
Main outcomes and measures: A main association of sex with regional tau in the entorhinal cortices, inferior temporal lobe, and a meta-region of interest, which was a composite of regions in the temporal lobe. Associations between sex and global Aβ as well as sex and APOE ε4 on these regions after controlling for age were also examined.
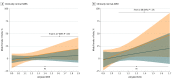
Results: The mean (SD) age of all individuals was 74.2 (7.6) years (81 APOE ε4 carriers [31%]; 89 individuals [30%] with high Aβ). There was no clear association of sex with regional tau that was replicated across studies. However, in both cohorts, clinically normal women exhibited higher entorhinal cortical tau than men (meta-analytic estimate: β [male] = -0.11 [0.05]; 95% CI, -0.21 to -0.02; P = .02), which was associated with individuals with higher Aβ burden. A sex by APOE ε4 interaction was not associated with regional tau (meta-analytic estimate: β [male, APOE ε4+] = -0.15 [0.09]; 95% CI, -0.32 to 0.01; P = .07).
Conclusions and relevance: Early tau deposition was elevated in women compared with men in individuals on the Alzheimer disease trajectory. These findings lend support to a growing body of literature that highlights a biological underpinning for sex differences in Alzheimer disease risk.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

