TGF-β Superfamily Regulation of Follicle-Stimulating Hormone Synthesis by Gonadotrope Cells: Is There a Role for Bone Morphogenetic Proteins?
- PMID: 30715256
- PMCID: PMC6388655
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2018-01038
TGF-β Superfamily Regulation of Follicle-Stimulating Hormone Synthesis by Gonadotrope Cells: Is There a Role for Bone Morphogenetic Proteins?
Abstract
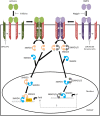
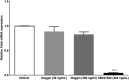
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are pleiotropic ligands in the TGF-β superfamily. In the early to mid-2000s, several BMPs, including BMP2, were shown to regulate FSH synthesis alone and in synergy with activins in immortalized gonadotrope-like cell lines and primary pituitary cultures. Activins are also TGF-β family members, which were identified and named based on their abilities to stimulate FSH production selectively. Mechanistic analyses suggested that BMP2 promoted expression of the FSHβ subunit gene (Fshb) via at least two nonmutually exclusive mechanisms. First, BMP2 stimulated the production of the inhibitor of DNA-binding proteins 1, 2, and 3 (Id1, Id2, and Id3), which potentiated the stimulatory actions of homolog of Drosophila mothers against decapentaplegic 3 (SMAD3) on the Fshb promoter. SMAD3 is an intracellular signaling protein that canonically mediates the actions of activins and is an essential regulator of Fshb production in vitro and in vivo. Second, BMP2 was shown to activate SMAD3-dependent signaling via its canonical type IA receptor, BMPR1A (also known as ALK3). This was a surprising result, as ALK3 conventionally activates distinct SMAD proteins. Although these initial results were compelling, they were challenged by contemporaneous and subsequent observations. For example, inhibitors of BMP signaling did not specifically impair FSH production in cultured pituitary cells. Of perhaps greater significance, mice lacking ALK3 in gonadotrope cells produced FSH normally. Therefore, the physiological role of BMPs in FSH synthesis in vivo is presently uncertain.
Copyright © 2019 Endocrine Society.
Figures
References
-
- Wozney JM, Rosen V, Celeste AJ, Mitsock LM, Whitters MJ, Kriz RW, Hewick RM, Wang EA. Novel regulators of bone formation: molecular clones and activities. Science. 1988;242(4885):1528–1534. - PubMed
-
- Hanamura H, Higuchi Y, Nakagawa M, Iwata H, Nogami H, Urist MR. Solubilized bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) from mouse osteosarcoma and rat demineralized bone matrix. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980; (148):281–290. - PubMed
-
- Nogami H, Oohira A. Postnatal new bone formation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984; (184):106–113. - PubMed
-
- Jones CM, Lyons KM, Hogan BL. Involvement of bone morphogenetic protein-4 (BMP-4) and Vgr-1 in morphogenesis and neurogenesis in the mouse. Development. 1991;111(2):531–542. - PubMed
-
- Lyons KM, Pelton RW, Hogan BL. Organogenesis and pattern formation in the mouse: RNA distribution patterns suggest a role for bone morphogenetic protein-2A (BMP-2A). Development. 1990;109(4):833–844. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

