SeqSleepNet: End-to-End Hierarchical Recurrent Neural Network for Sequence-to-Sequence Automatic Sleep Staging
- PMID: 30716040
- PMCID: PMC6481557
- DOI: 10.1109/TNSRE.2019.2896659
SeqSleepNet: End-to-End Hierarchical Recurrent Neural Network for Sequence-to-Sequence Automatic Sleep Staging
Abstract
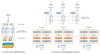
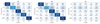
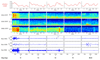
Automatic sleep staging has been often treated as a simple classification problem that aims at determining the label of individual target polysomnography epochs one at a time. In this paper, we tackle the task as a sequence-to-sequence classification problem that receives a sequence of multiple epochs as input and classifies all of their labels at once. For this purpose, we propose a hierarchical recurrent neural network named SeqSleepNet (source code is available at http://github.com/pquochuy/SeqSleepNet). At the epoch processing level, the network consists of a filterbank layer tailored to learn frequency-domain filters for preprocessing and an attention-based recurrent layer designed for short-term sequential modeling. At the sequence processing level, a recurrent layer placed on top of the learned epoch-wise features for long-term modeling of sequential epochs. The classification is then carried out on the output vectors at every time step of the top recurrent layer to produce the sequence of output labels. Despite being hierarchical, we present a strategy to train the network in an end-to-end fashion. We show that the proposed network outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches, achieving an overall accuracy, macro F1-score, and Cohen's kappa of 87.1%, 83.3%, and 0.815 on a publicly available dataset with 200 subjects.
Figures



References
-
- Institute of Medicine. Sleep Disorders and Sleep Deprivation: An Unmet Public Health Problem. Washington DC: The National Academies Press; 2006. - PubMed
-
- Krieger AC, editor. Social and Economic Dimensions of Sleep Disorders, An Issue of Sleep Medicine Clinics. Elsevier; 2017.
-
- Iber C, et al. The AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events: Rules, terminology and technical specifications. American Academy of Sleep Medicine. 2007
-
- Hobson JA. A manual of standardized terminology, techniques and scoring system for sleep stages of human subjects. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology. 1969;26(6):644.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

