Internal Doses of Glycidol in Children and Estimation of Associated Cancer Risk
- PMID: 30717263
- PMCID: PMC6468878
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics7010007
Internal Doses of Glycidol in Children and Estimation of Associated Cancer Risk
Abstract
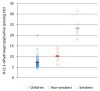
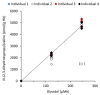
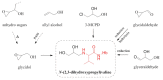
The general population is exposed to the genotoxic carcinogen glycidol via food containing refined edible oils where glycidol is present in the form of fatty acid esters. In this study, internal (in vivo) doses of glycidol were determined in a cohort of 50 children and in a reference group of 12 adults (non-smokers and smokers). The lifetime in vivo doses and intakes of glycidol were calculated from the levels of the hemoglobin (Hb) adduct N-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)valine in blood samples from the subjects, demonstrating a fivefold variation between the children. The estimated mean intake (1.4 μg/kg/day) was about two times higher, compared to the estimated intake for children by the European Food Safety Authority. The data from adults indicate that the non-smoking and smoking subjects are exposed to about the same or higher levels compared to the children, respectively. The estimated lifetime cancer risk (200/10⁵) was calculated by a multiplicative risk model from the lifetime in vivo doses of glycidol in the children, and exceeds what is considered to be an acceptable cancer risk. The results emphasize the importance to further clarify exposure to glycidol and other possible precursors that could give a contribution to the observed adduct levels.
Keywords: Hb adduct; N-(2.3-dihydroxypropyl)valine; UPLC/MS/MS; cancer risk; glycidol; in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures
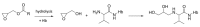

References
-
- Nadler D.L., Zurbenko I.G. Estimating Cancer Latency Times Using a Weibull Model. Adv. Epidemiol. 2014;2014:8. doi: 10.1155/2014/746769. - DOI
-
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) Risks for human health related to the presence of 3- and 2-monochloropropanediol (MCPD), and their fatty acid esters, and glycidyl fatty acid esters in food. EFSA J. 2016;14:159.
-
- BfR (Federal Institute for Risk Assessment) Initial Evaluation of the Assessment of Levels of Glycidol Fatty Acid Esters Detected in Refined Vegetable Fats. [(accessed on 30 March 2009)];2009 Available online: https://mobil.bfr.bund.de/cm/349/initial_evaluation_of_the_assessment_of....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

