Mortality among pediatric patients on HIV treatment in sub-Saharan African countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 30717720
- PMCID: PMC6360742
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-019-6482-1
Mortality among pediatric patients on HIV treatment in sub-Saharan African countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Despite substantial improvements in accessibility of Anti-Retroviral Treatment (ART), death of children on ART remains a prevailing challenge in sub-Saharan African (SSA) countries. However, the pooled magnitude of mortality at different ART follow-up periods remains unknown for the region. We estimated the pooled proportion of all-cause mortality for pediatric patients receiving first-line ART at 3, 6, 12, and 24 months follow-up period in SSA.
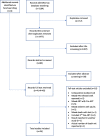
Methods: We searched for relevant articles published between January 2014 and June 2018 on PubMed, Hinari and Google scholar databases. We searched for additional articles from reference lists and 2014-2018 abstracts archived by the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI) and the International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science (IAS).
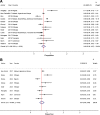
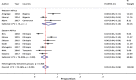
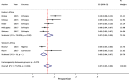
Results: We reviewed 29 articles reporting mortality among pediatric ART patients at different follow-up periods in countries from 2001 to 2016. Among the 51,619 pediatric ART patients in these cohorts, studies reported 4061 (7.9%) all-cause cumulative death. The cumulative pooled proportion of mortality at 3, 6, 12 and 24 months of ART were 3% (95% CI: 3.0-4.0), 5% (95% CI: 4.0-6.0), 6% (95% CI: 5.0-7.0) and 7% (95% CI: 6.0-8.0), respectively.
Conclusions: In SSA, significant proportion of mortality among children occurs in the first 3-6 months of ART initiation. Western Africa has a little higher estimate of mortality among pediatric ART patients at 6 and 12 months of follow-up. Strategies to prevent early mortality including thorough screening and management of opportunistic infections before ART initiation are needed.
Keywords: Children; Meta-analysis; Mortality; Pediatric; Sub-Saharan Africa; Systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ information
IA: MPH; Chief Public Health Professional, PhDc at University of Gondar, Ethiopia. He has expertise in HIV/AIDS program and research. SL: MPH, PhD; Research Fellow at London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, based at Ethiopian Public Health Institute, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. She has expertise in research.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . Consolidated guidelines on the use of antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV infection: recommendations for a public health approach. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

