The Correlation between the Frontostriatal Network and Impulsivity in Internet Gaming Disorder
- PMID: 30718701
- PMCID: PMC6361914
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-37702-4
The Correlation between the Frontostriatal Network and Impulsivity in Internet Gaming Disorder
Abstract
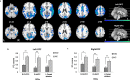
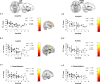
As excessive use of internet gaming has become a serious public health concern, increasing studies have revealed that impulsivity is one of the important risk factors of internet gaming disorder (IGD). This study was designed to investigate the altered resting-state functional connectivity (FC) of the bilateral orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) in IGD participants and to examine its relationship with impulsivity compared with the normal controls (NC). Seed-based analyses verified that participants with IGD displayed decreased FC between the OFC and frontal, striatal, temporal and occipital regions different from NC. Moreover, IGD participants showed weankened FC from the OFC with dorsal anterior cingulate cortex as well as with dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and dorsal striatum as the results of group difference. These results could suggest that the decreased frontostriatal connectivity was associated with excessive internet gaming. Also, the increased FC in frontostriatal regions was correlated with impulse control in the NC but not the IGD participants. Further insight into the brain circuitry on frontostriatal could provide the target for developing treatment approaches of impulse control in IGD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Abnormal prefrontal cortex resting state functional connectivity and severity of internet gaming disorder.Brain Imaging Behav. 2016 Sep;10(3):719-29. doi: 10.1007/s11682-015-9439-8. Brain Imaging Behav. 2016. PMID: 26311395
-
Altered gray matter density and disrupted functional connectivity of the amygdala in adults with Internet gaming disorder.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2015 Mar 3;57:185-92. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2014.11.003. Epub 2014 Nov 13. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25448779
-
Frontostriatal circuits, resting state functional connectivity and cognitive control in internet gaming disorder.Addict Biol. 2017 May;22(3):813-822. doi: 10.1111/adb.12348. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Addict Biol. 2017. PMID: 26769234
-
The prefrontal dysfunction in individuals with Internet gaming disorder: a meta-analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging studies.Addict Biol. 2015 Jul;20(4):799-808. doi: 10.1111/adb.12154. Epub 2014 Jun 3. Addict Biol. 2015. PMID: 24889021 Review.
-
Neurobiological correlates of internet gaming disorder: Similarities to pathological gambling.Addict Behav. 2017 Jan;64:349-356. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2015.11.004. Epub 2015 Nov 24. Addict Behav. 2017. PMID: 26621112 Review.
Cited by
-
Neural mechanisms of behavioral addiction: An ALE meta-analysis and MACM analysis.J Behav Addict. 2025 Jan 24;14(1):18-38. doi: 10.1556/2006.2024.00082. Print 2025 Mar 28. J Behav Addict. 2025. PMID: 39853319 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneity of gaming disorder: A clinically-based typology for developing personalized interventions.J Behav Addict. 2023 Nov 7;12(4):855-861. doi: 10.1556/2006.2023.00059. Print 2023 Dec 22. J Behav Addict. 2023. PMID: 37934288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PET Hypometabolism of the Prefrontal-Cingulate Cortices in Internet Gaming Disorder.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Jan 15;11:566518. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.566518. eCollection 2020. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33519539 Free PMC article.
-
Regional brain activity of resting-state fMRI and auditory oddball ERP with multimodal approach in individuals with internet gaming disorder.J Behav Addict. 2023 Nov 21;12(4):895-906. doi: 10.1556/2006.2023.00063. Print 2023 Dec 22. J Behav Addict. 2023. PMID: 37987778 Free PMC article.
-
The Mediating Effects of Affect on Associations between Impulsivity or Resilience and Internet Gaming Disorder.J Clin Med. 2019 Jul 25;8(8):1102. doi: 10.3390/jcm8081102. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31349640 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Durkee, T. et al. Prevalence of pathological internet use among adolescents in Europe: demographic and social factors. Addiction, 2210–2222, 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2012.03946.x (2012). - PubMed
-
- Kuss DJ, Griffiths MD. Internet Gaming Addiction: A Systematic Review of Empirical Research. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction. 2011;10:278–296. doi: 10.1007/s11469-011-9318-5. - DOI
-
- Smith KL, Hummer TA, Hulvershorn LA. Pathological Video Gaming and Its Relationship to Substance Use Disorders. Current Addiction Reports. 2015;2:302–309. doi: 10.1007/s40429-015-0075-6. - DOI
-
- Edition, F. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. (Am Psychiatric Assoc, 2013).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

