An essential role for the Zn2+ transporter ZIP7 in B cell development
- PMID: 30718914
- PMCID: PMC6561116
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-018-0295-8
An essential role for the Zn2+ transporter ZIP7 in B cell development
Abstract
Despite the known importance of zinc for human immunity, molecular insights into its roles have remained limited. Here we report a novel autosomal recessive disease characterized by absent B cells, agammaglobulinemia and early onset infections in five unrelated families. The immunodeficiency results from hypomorphic mutations of SLC39A7, which encodes the endoplasmic reticulum-to-cytoplasm zinc transporter ZIP7. Using CRISPR-Cas9 mutagenesis we have precisely modeled ZIP7 deficiency in mice. Homozygosity for a null allele caused embryonic death, but hypomorphic alleles reproduced the block in B cell development seen in patients. B cells from mutant mice exhibited a diminished concentration of cytoplasmic free zinc, increased phosphatase activity and decreased phosphorylation of signaling molecules downstream of the pre-B cell and B cell receptors. Our findings highlight a specific role for cytosolic Zn2+ in modulating B cell receptor signal strength and positive selection.
Figures



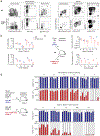
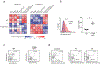
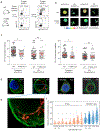


Comment in
-
Revisiting the old and learning the new of zinc in immunity.Nat Immunol. 2019 Mar;20(3):248-250. doi: 10.1038/s41590-019-0319-z. Nat Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30718916 No abstract available.
References
-
- Vetrie D, et al., The gene involved in X-linked agammaglobulinaemia is a member of the src family of protein-tyrosine kinases. Nature, 1993. 361(6409): p. 226–33. - PubMed
-
- Tsukada S, et al., Deficient expression of a B cell cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase in human X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Cell, 1993. 72(2): p. 279–90. - PubMed
-
- Aw A and Brown JR, Current Status of Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Development and Use in B-Cell Malignancies. Drugs Aging, 2017. 34(7): p. 509–527. - PubMed
-
- Durandy A, Kracker S, and Fischer A, Primary antibody deficiencies. Nat Rev Immunol, 2013. 13(7): p. 519–33. - PubMed
References for Online Methods
-
- Picelli S, et al., Full-length RNA-seq from single cells using Smart-seq2. Nat Protoc, 2014. 9(1): p. 171–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MR/L020149/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 19270/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- MR/R007748/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K023667/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/M012646/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L02036X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K001981/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00008/6/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- P01 AI061093/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L001209/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/N00275X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/M009971/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_15065/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/N020472/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AI104857/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MR/R010676/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/R017549/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

